The 4 step process to overcome any weakness provides a structured approach to identifying and addressing personal shortcomings. This isn’t about simply ignoring your flaws, but rather understanding their roots and developing actionable strategies to improve. We’ll delve into the crucial steps of acknowledging your weaknesses, understanding their origins, creating effective improvement plans, and finally, consistently practicing and monitoring your progress.
This comprehensive guide covers the essential aspects of personal development, offering practical insights and actionable advice. It moves beyond theoretical concepts and dives into tangible examples, demonstrating how to transform perceived weaknesses into strengths.
Defining Weakness
Understanding weaknesses is crucial for personal growth. They are not inherent flaws, but rather areas where our skills are underdeveloped or lacking compared to our desired performance levels. A proper definition helps us to accurately pinpoint these areas and develop strategies to address them effectively. A nuanced understanding separates weaknesses from simply not possessing a particular skill, which can be a critical distinction for fostering self-improvement.
A Comprehensive Definition of Weakness
Weaknesses, in the context of personal development, are areas where an individual consistently performs below their desired or potential level of competence. They represent gaps in skill, knowledge, or habits that hinder progress toward personal goals. These gaps can manifest in various forms, including emotional responses, decision-making processes, or specific tasks. Importantly, weaknesses are not static; they can be modified and improved through focused effort and learning.
Weakness vs. Underdeveloped Skill
A key distinction lies between a weakness and an underdeveloped skill. A weakness implies a consistent struggle and negative impact on performance, whereas an underdeveloped skill simply needs further development. For example, someone might struggle with public speaking (a weakness) due to anxiety and lack of practice. Conversely, someone might not be skilled at public speaking yet, but with practice and coaching, they could significantly improve.
This difference in approach is vital to tailor effective improvement strategies.
Want to conquer those nagging weaknesses? The 4-step process is a game-changer. It’s all about identifying the weakness, understanding its root cause, developing a targeted action plan, and finally, consistently implementing it. This approach, combined with adopting some amazing strategies like the ones found in 9 awesome strategies for living more energized life , can significantly boost your overall well-being.
Ultimately, the key to overcoming any weakness lies in a well-structured plan and a positive mindset, ensuring a more empowered and vibrant you.
Cultural and Individual Perceptions of Weakness
Perceptions of weakness vary across cultures and individuals. Some cultures may value certain traits over others, which can impact how an individual views their shortcomings. For instance, a culture that prioritizes collectivism may view assertiveness as a weakness, while a culture that emphasizes individualism may view a lack of assertiveness as a weakness. Self-awareness and understanding cultural contexts are vital to identifying personal weaknesses without bias.
Identifying Your Own Weaknesses
Identifying personal weaknesses requires self-reflection and honest assessment. This process involves introspection and consideration of feedback from trusted sources. A few methods include:
- Analyzing past experiences: Reflecting on situations where you struggled or experienced setbacks can reveal patterns and recurring challenges.
- Seeking feedback from others: Honest feedback from mentors, friends, and colleagues can provide valuable insights into areas where you might be falling short.
- Self-assessment questionnaires: Using validated questionnaires designed to assess personality traits, skills, or habits can offer objective data.
- Identifying areas of discomfort: Recognizing activities or situations that evoke stress, anxiety, or hesitation can point to underlying weaknesses.
A Framework for Addressing Weaknesses
This table provides a structured approach to understanding and addressing personal weaknesses.
| Weakness | Impact | Possible Solutions | Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procrastination | Missed deadlines, decreased productivity, increased stress | Time management techniques, breaking down tasks, setting realistic goals | Establish a routine, prioritize tasks, reward completion |
| Poor communication | Misunderstandings, conflicts, strained relationships | Active listening, clear articulation, seeking feedback | Practice expressing ideas, joining communication groups, taking a course |
| Fear of public speaking | Avoidance of opportunities, nervousness, anxiety | Practice, seeking feedback, joining a public speaking group | Start small, focus on delivery, visualization techniques |
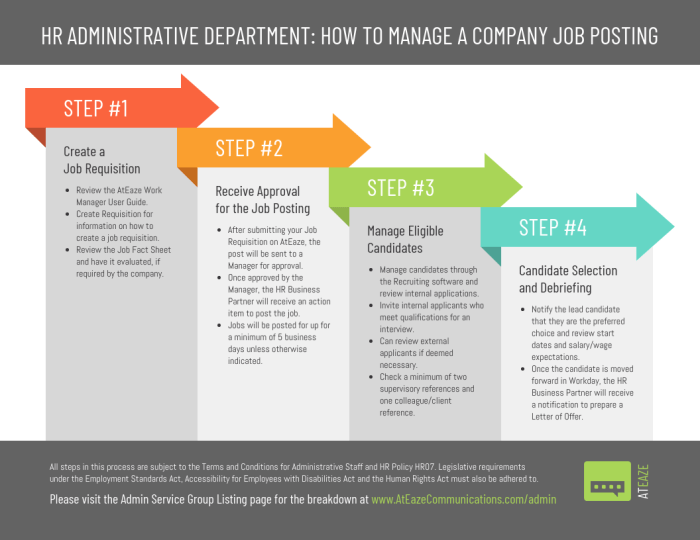
Understanding the 4-Step Process
Embarking on a journey to overcome a weakness requires a structured approach. This isn’t about a quick fix; it’s about cultivating a sustainable change. The 4-step process provides a roadmap, guiding you through the essential stages of identification, understanding, action, and reinforcement. Each step is crucial, building upon the previous one to create a solid foundation for lasting improvement.This comprehensive process allows for a deeper understanding of the root causes of a weakness, enabling a more effective and targeted strategy for overcoming it.
By breaking down the process into manageable steps, you can approach the challenge with a clear plan of action, boosting your confidence and increasing your likelihood of success.
Defining the Four Steps
The four-step process for overcoming weaknesses involves a methodical approach that goes beyond simply acknowledging a problem. It requires a commitment to self-reflection and active implementation of strategies. Each step plays a vital role in the overall journey of personal growth.
Want to conquer those pesky weaknesses? A four-step process can help you do just that. First, identify the weakness. Then, research and understand it. Next, create a concrete plan to address it, focusing on manageable steps.
Finally, stick to your plan, and remember that overcoming weaknesses takes time and consistent effort. And, while you’re working on those weaknesses, you might want to consider what you’re eating before bed. For example, avoiding foods that can disrupt your sleep cycle, like those listed in dont want another sleepless night avoid these 8 foods , is crucial for a good night’s rest.
This, in turn, can bolster your overall strength to deal with whatever weaknesses you face.
| Step | Description | Significance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Acknowledge and Define the Weakness | This initial step involves identifying the specific weakness you want to address. It’s not enough to simply say you’re “bad at public speaking.” Instead, pinpoint the precise area of weakness—e.g., difficulty articulating thoughts clearly, fear of eye contact, or lack of preparation. | This foundational step lays the groundwork for the entire process. Without a clear definition, targeted solutions cannot be developed. Precisely defining the weakness allows for the development of strategies tailored to the specific nature of the problem. | A student struggling with math might define their weakness as difficulty understanding algebraic equations, rather than simply saying they are “bad at math.” |
| 2. Understand the Root Cause | Once the weakness is defined, delve into the underlying reasons why you exhibit that weakness. Consider past experiences, emotional factors, or ingrained habits. Ask yourself: What triggers this weakness? What are the potential contributing factors? | Understanding the root cause is crucial for developing effective strategies. If you know the triggers, you can create preventative measures. Addressing the underlying reasons for the weakness leads to more sustainable change. | If a person struggles with procrastination, they might uncover that their fear of failure or perfectionism is a root cause. |
| 3. Implement Actionable Strategies | This step involves developing and implementing specific strategies to address the identified weakness. These strategies should be realistic, achievable, and measurable. Create a plan with concrete steps to help you improve. | Action is the cornerstone of any improvement process. Without putting your strategies into practice, the process remains theoretical. The implementation stage involves active steps toward change, building a tangible improvement over time. | To overcome a fear of public speaking, a person might start by practicing presentations in front of a small group of friends or family, gradually increasing the size of the audience. |
| 4. Reinforce and Maintain the Improvement | The final step focuses on maintaining the improvements made. This involves continuous reinforcement of the new behaviors and strategies. Regular practice, seeking feedback, and acknowledging progress are crucial components. | Sustaining progress is as important as achieving it. This step ensures that the improvements become integrated into your daily life. Regular reinforcement prevents the weakness from resurfacing. | To maintain improved public speaking skills, a person might join a Toastmasters club or actively seek feedback on their presentations. |
Comparison with Other Methods
Numerous personal development methods exist. While various approaches offer valuable insights, the 4-step process distinguishes itself by focusing on a deep understanding of the weakness’s root causes. Unlike some methods that emphasize general self-improvement techniques, this process provides a structured approach to targeted weakness elimination.
Step 1: Acknowledgment and Acceptance

Overcoming weaknesses isn’t about magically eliminating them, but about understanding and managing them effectively. This first step, acknowledging and accepting your weaknesses, is the foundation for any meaningful progress. It’s not about ignoring or pretending they don’t exist, but about recognizing them with clarity and approaching them with a constructive mindset.This step involves more than just admitting you have flaws; it’s about accepting those flaws without judgment or self-criticism.
It’s about understanding that weaknesses are an integral part of being human and that they are opportunities for growth and improvement, not failures to be ashamed of.
The Crucial Role of Acknowledgment
Acknowledging your weaknesses is the first, and often the most challenging, step in the process. It involves honestly confronting the areas where you struggle and recognizing their impact on your life. This isn’t about dwelling on negativity; instead, it’s about gaining a clear perspective on your limitations. This understanding is essential for subsequent steps in the process. It allows you to approach solutions with a clearer picture of the problem.
The Significance of Accepting Your Weaknesses
Accepting your weaknesses involves understanding that they are not inherently bad or negative. Instead, they represent areas where you can improve and grow. This acceptance is crucial because it releases you from the pressure of perfection and allows you to focus on developing strategies for improvement. Judgment and self-criticism only hinder progress. Instead, embrace a growth mindset.
Methods to Acknowledge and Accept Weaknesses Constructively
To acknowledge and accept weaknesses constructively, practice self-reflection and introspection. Ask yourself questions like: What are my typical reactions in challenging situations? What are the patterns in my behaviors that lead to difficulties? What are my strengths that can complement my weaknesses? By understanding your patterns, you can gain insights into your behaviors and learn how to approach them in a constructive way.Furthermore, seek feedback from trusted individuals.
This feedback can provide valuable insights into areas where you might be unaware of your weaknesses. Be open to hearing constructive criticism and use it to gain a more comprehensive understanding of yourself.
Contrasting Denial and Acceptance
| Feature | Denial | Acceptance ||—|—|—|| Perspective | Avoiding confronting weaknesses, pretending they don’t exist | Acknowledging weaknesses and understanding their impact || Impact on Progress | Hinders progress as issues remain unaddressed | Facilitates progress as you can develop solutions || Example | A student consistently procrastinates on assignments, telling themselves they’ll “figure it out later.” | The same student recognizes procrastination as a weakness, and actively seeks strategies to manage their time more effectively.
|| Example | An employee avoids tasks they find challenging, believing they are incapable of completing them. | The same employee identifies the challenging tasks as areas for development, and actively seeks mentorship and training to improve. |
Self-Reflection and Introspection
Self-reflection and introspection are powerful tools in the acceptance process. They involve looking inward and honestly assessing your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. By understanding the root causes of your weaknesses, you can begin to develop strategies for overcoming them. It’s a journey of self-discovery, allowing you to understand the reasons behind your actions and identify areas for growth.
This self-awareness is the key to personal development and improvement.
Step 2: Understanding the Root Cause
Unveiling the hidden reasons behind a weakness is crucial for effective improvement. Simply acknowledging a weakness isn’t enough; understanding its origins allows for targeted and impactful solutions. This step delves into the past experiences and behaviors that have shaped the weakness, providing a foundation for constructive change. This exploration isn’t about assigning blame but rather about understanding the factors that have contributed to the current situation.Identifying the root cause is akin to excavating the foundation of a house.
A wobbly floor might be due to a faulty foundation (the root cause), not just a loose floorboard. Addressing the root cause strengthens the entire structure, ensuring lasting stability and resilience. By exploring the underlying reasons, we can move beyond superficial fixes and build sustainable strategies for overcoming the weakness.
Identifying Underlying Causes
Understanding the root causes of a weakness requires a proactive approach, moving beyond superficial explanations. It necessitates a careful examination of past experiences and behaviors that have contributed to the development of the weakness. This exploration involves self-reflection, potentially with the assistance of trusted mentors or therapists.
Exploring Past Experiences and Behaviors
Past experiences and behaviors play a significant role in shaping our present weaknesses. For example, a fear of public speaking might stem from a past negative experience, like a poorly received presentation. Identifying these experiences, even seemingly minor ones, is critical to understanding the deeper roots of the weakness. Understanding these experiences can reveal patterns or triggers that contribute to the current manifestation of the weakness.
Methods for Exploring Root Causes
Several methods can be employed to uncover the root causes of a weakness. Journaling, where you document thoughts, feelings, and experiences related to the weakness, can be highly effective. Talking to trusted friends, family members, or mentors can offer valuable perspectives. Seeking professional guidance from therapists or counselors can provide further insight into the underlying psychological factors influencing the weakness.
Analyzing past situations, noting the circumstances and reactions involved, is crucial in recognizing recurring patterns that contribute to the weakness.
Comparing Approaches to Identifying Root Causes
| Method | Description | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Journaling | Recording thoughts, feelings, and experiences related to the weakness. | Provides a detailed record of personal experiences, promotes introspection. | May not be sufficient for complex issues; requires consistent effort. |
| Seeking Professional Guidance | Consulting therapists or counselors for professional insight. | Provides a structured approach, offers objective feedback, addresses potential psychological factors. | Can be expensive and time-consuming; requires vulnerability. |
| Analyzing Past Situations | Examining past situations, noting circumstances and reactions. | Helps identify recurring patterns and triggers, facilitates self-awareness. | Requires significant self-reflection and can be emotionally challenging. |
| Talking to Trusted Individuals | Discussing the weakness with trusted individuals. | Offers diverse perspectives, provides emotional support. | May not always lead to objective analysis; potentially influenced by the listener’s biases. |
Avoiding External Blame, The 4 step process to overcome any weakness
It’s essential to avoid blaming others or external factors for a weakness. While external pressures may contribute to a weakness, focusing on personal responsibility is crucial for effective change. Identifying the root cause is about internal reflection, not external justification. A strong focus on personal responsibility enables the development of sustainable strategies for overcoming the weakness. A mindset of personal responsibility fosters proactive and effective change.
Instead of blaming others, focus on the actions you can take to address the underlying issues.
Step 3: Developing Strategies for Improvement: The 4 Step Process To Overcome Any Weakness
Overcoming weaknesses isn’t just about recognizing and understanding them; it’s about actively creating and implementing strategies to address them. This crucial step requires a proactive approach, turning insights into actionable plans. Effective strategies aren’t one-size-fits-all; they must be tailored to the specific weakness and the individual’s circumstances.Developing strategies for improvement involves a systematic approach to transforming weaknesses into strengths.
It’s not enough to simply identify a weakness; you need to translate that understanding into a concrete plan of action. This process requires careful consideration of various factors, including personal strengths, available resources, and potential challenges.
Crafting Actionable Strategies
Developing effective strategies involves a structured framework. A crucial aspect is the specificity of the strategy. Vague goals, such as “improve communication,” are less effective than precise ones like “improve active listening skills by practicing reflecting back what I hear from others.” This clarity is essential for measuring progress and ensuring focused effort.
A Framework for Strategy Development
A structured approach is key to developing effective improvement strategies. This framework involves several key components:
- Clearly Defined Goals: Begin by defining precise, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For instance, instead of “improve time management,” a SMART goal might be “reduce project completion time by 20% within the next three months by implementing a time-blocking schedule.” This provides a clear target and allows for tracking progress.
- Specific Actions: Identify concrete actions that will contribute to achieving the goals. If the goal is to improve decision-making, actions might include researching multiple perspectives before making a choice or creating a decision-making checklist. These actions are crucial steps toward achieving the desired outcome.
- Resource Allocation: Assess the resources needed to implement the strategies. This might include time, tools, or support systems. For instance, if the strategy involves learning a new software, the resources might include the cost of the software, access to training materials, and time dedicated to learning.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a system for tracking progress and evaluating the effectiveness of the strategies. This involves setting milestones, tracking key metrics, and adjusting strategies as needed. For example, if a strategy to improve communication involves more frequent check-ins, monitor the frequency and note if it’s improving or not.
Examples of Actionable Strategies
Here are some actionable strategies for addressing common weaknesses:
| Weakness | Actionable Strategy |
|---|---|
| Time Management | Create a detailed weekly schedule, prioritize tasks using the Eisenhower Matrix, and utilize time-blocking techniques. |
| Communication | Practice active listening, use clear and concise language, and seek feedback from others on communication style. |
| Decision Making | Develop a structured decision-making process, research various options thoroughly, and consider potential risks and rewards. |
| Public Speaking | Practice presentations in front of a mirror or small group, focus on clear articulation and confident body language, and seek constructive criticism. |
Comparing Approaches to Improvement Plans
Various approaches can be employed for developing effective improvement plans. Some common approaches include:
- The Coaching Approach: Seeking guidance from a mentor or coach who can provide support and feedback during the implementation process.
- The Self-Directed Approach: Developing and implementing the plan independently, utilizing available resources and self-discipline.
- The Group Approach: Collaborating with a support group or team to share experiences, provide motivation, and hold each other accountable.
Step 4
Consistency is key to solidifying improvements and overcoming weaknesses. Simply identifying and understanding a weakness isn’t enough. The true test lies in the consistent effort to apply the strategies developed to cultivate positive change. This final step emphasizes the importance of sustained practice and monitoring progress to ensure long-term success.The path to improvement isn’t a sprint, but a marathon.
It requires dedication and a commitment to regular practice, coupled with ongoing evaluation of the effectiveness of the strategies employed. Regular monitoring allows for necessary adjustments, ensuring that efforts remain focused and efficient.
Consistent Practice
Sustained effort is crucial for the successful implementation of improvement strategies. Without consistent practice, the acquired knowledge and insights may remain theoretical, failing to translate into tangible results. Regular practice builds muscle memory and reinforces the desired behaviors or skills. Think of learning a musical instrument; sporadic practice will not yield the same results as daily, dedicated sessions.
Monitoring Progress
Monitoring progress is not just about tracking numbers; it’s about assessing the effectiveness of strategies and making necessary adjustments. Regular evaluations allow you to identify areas where strategies are working well and where they need refinement. This proactive approach to monitoring enables you to stay on track and adapt to challenges or unexpected roadblocks. By consistently monitoring progress, you can stay motivated and on track toward your goals.
Methods for Maintaining Consistency
Creating a structured routine and incorporating practice into your daily schedule can greatly improve consistency. Setting realistic goals, breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and utilizing tools like calendars or reminders can enhance adherence to the practice schedule. Finding a practice partner or joining a support group can also provide motivation and accountability. Leveraging technology, such as habit-tracking apps, can be extremely helpful in staying on track.
Progress Monitoring Plan
| Week | Focus Area | Specific Strategy | Target Goal | Progress Assessment (Scale 1-5, 5 being Excellent) | Adjustments Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Time Management | Prioritization Matrix | Complete 3 high-priority tasks daily | 3 | None, maintain current approach |
| 2 | Time Management | Time Blocking | Allocate specific time slots for tasks | 4 | Refine time allocation for tasks requiring more focused attention. |
| 3 | Communication | Active Listening | Maintain eye contact and ask clarifying questions during conversations | 2 | Practice active listening techniques with a friend or colleague. |
| 4 | Communication | Non-verbal cues | Employ appropriate body language and tone | 3 | Review communication styles and improve nonverbal cues in different situations. |
Adjusting Strategies
Regular evaluation of progress is essential. If a strategy isn’t yielding the desired results, adjustments are necessary. Feedback from practice sessions or interactions with others can highlight areas for improvement. Consider the root cause of any observed setbacks and modify the strategy accordingly. For instance, if a time management technique isn’t working, explore alternative strategies like delegation or task simplification.
Figuring out how to conquer personal weaknesses is a journey, not a sprint. A four-step process can help – first, identifying the weakness, then understanding its root cause, followed by developing a targeted strategy, and finally, consistently practicing the new skill. Considering whether or not blogs are a worthwhile investment for businesses, as explored in this article on do blogs really make sense for all companies , can be similarly approached.
Ultimately, the core principle of proactively addressing any weakness, whether it’s in your personal life or a business strategy, remains the same.
Adapting strategies based on feedback and results is a key element in the improvement process.
Illustrative Examples
Applying the 4-step process to overcome weaknesses isn’t theoretical; it’s a practical tool for personal and professional growth. By understanding and actively engaging with each step, individuals can transform perceived limitations into strengths. This section provides concrete examples to illustrate how the process works in real-world scenarios.
Public Speaking Anxiety
Overcoming public speaking anxiety often involves a deep dive into understanding the root causes. For many, the fear stems from a combination of past experiences, self-doubt, and a perceived lack of competence. By acknowledging and accepting these anxieties, individuals can begin the journey towards improvement.
- Defining the Weakness: Recognizing public speaking as a weakness that hinders professional and social opportunities.
- Understanding the Root Cause: Identifying past negative experiences, such as feeling judged or criticized during presentations. Understanding that fear is often rooted in the perceived expectations of others.
- Developing Strategies for Improvement: Implementing techniques like practicing in front of a mirror, joining Toastmasters clubs, or focusing on breathing exercises. Creating a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable practicing their skills.
- Acknowledgment and Acceptance: Acknowledging that fear is normal, and that everyone experiences it differently. Accepting the process as a journey with ups and downs.
| Category | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Confidence Level | Low, hesitant, often avoided public speaking engagements | Increased confidence, comfortable delivering presentations, and engaging with the audience |
| Presentation Quality | Rambling, lack of structure, high anxiety | Clear, concise, and well-structured presentations, better engagement with the audience |
| Impact | Negative impact on professional and social opportunities | Positive impact on presentations and career advancement |
Time Management Challenges
Time management issues often arise from poor planning, unrealistic expectations, or procrastination. Identifying these underlying causes is key to developing effective solutions.
- Defining the Weakness: Inability to effectively manage time, leading to missed deadlines and decreased productivity.
- Understanding the Root Cause: Procrastination, poor prioritization, and difficulty saying “no” to commitments.
- Developing Strategies for Improvement: Implementing time-blocking techniques, using to-do lists, and establishing clear priorities. Learning to delegate tasks and say “no” to commitments that don’t align with priorities.
- Acknowledgment and Acceptance: Acknowledging the need for change and accepting that improvement takes time and effort.
| Category | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity | Low productivity, missed deadlines | Increased productivity, consistent achievement of goals and deadlines |
| Stress Levels | High stress due to overwhelming workload | Lower stress levels due to better time management |
| Work-Life Balance | Poor work-life balance, feeling overwhelmed | Improved work-life balance, greater sense of control over time |
Case Studies
- Social Anxiety: Identifying triggers, practicing social interactions in safe environments, and developing coping mechanisms. Real-life examples of overcoming social anxiety and building confidence in social situations.
- Procrastination: Understanding the root causes of procrastination, using time management strategies, and setting realistic goals. Real-life stories of individuals successfully overcoming procrastination.
- Poor Communication Skills: Identifying areas of weakness in communication, practicing active listening, and developing clear and concise communication styles. Real-world examples of how improved communication impacts relationships and career advancement.
Professional and Personal Growth
The 4-step process isn’t limited to overcoming weaknesses; it’s a framework for continuous personal and professional growth. By applying this process, individuals can identify areas for improvement, develop strategies for enhancement, and ultimately achieve their full potential.
Visual Representation
A strong visual representation of the 4-step process to overcome weaknesses is crucial for comprehension and retention. A well-designed infographic can effectively communicate the steps, making the process accessible and engaging for a wider audience. This visual aid can also serve as a handy reference tool for individuals seeking to improve themselves.Visual aids, such as infographics, are proven effective tools for conveying complex information in a clear and concise manner.
They enhance understanding by presenting data and processes in a more engaging and easily digestible format.
Infographic Design
This infographic will utilize a clean, modern design aesthetic. The overall color palette will be a combination of calming blues and greens, transitioning to warmer tones as the process progresses, reflecting the journey of overcoming a weakness. The layout will be organized in a clear, linear progression, following the four steps of the process. Each step will be represented by a distinct icon or symbol, making it easy to identify and understand each stage.
The use of clear and concise text will accompany each step, ensuring the infographic is easily understandable.
Infographic Elements and Significance
- Step 1: Acknowledgment and Acceptance: This step will be represented by an upward-pointing, partially opened book icon, signifying the act of acknowledging and accepting the weakness. The color will be a soft, calming blue, reflecting the initial stage of self-awareness.
- Step 2: Understanding the Root Cause: This step will be represented by a magnifying glass icon, hinting at the investigative nature of identifying the root cause. The color will be a slightly deeper shade of blue, indicating a more in-depth analysis. The background of this section can feature a flowchart-like structure to visually depict the process of analysis.
- Step 3: Developing Strategies for Improvement: This step will be represented by a gear or cog icon, highlighting the active process of developing solutions. The color will shift to a lighter, more energetic green, symbolizing the transition from passive acceptance to proactive action.
- Step 4: Illustrative Examples: This step will be represented by a brightly colored, graphic image of a person successfully completing a task related to the weakness. The color will transition to a vibrant green, emphasizing the successful outcome and achievement. This section could include brief, easily understood case studies or examples.
Key Takeaways from the Infographic
The infographic will aim to highlight the sequential nature of the process. It should emphasize that each step builds upon the previous one, forming a comprehensive strategy for overcoming any weakness. The visual representation will aim to create a clear pathway, demonstrating the steps required to transform a weakness into a strength. The visual elements will aim to convey a sense of accomplishment and empowerment.
Examples of Similar Infographics
Numerous infographics follow similar structures, often employing icons, colors, and text to present information. A notable example is a study published by Harvard Business Review on team building, utilizing icons to visually represent various aspects of team dynamics. Another example is a financial infographic, which utilizes color-coded bars and charts to visually represent data, allowing viewers to quickly grasp key trends and insights.
These infographics, while differing in their specific content, demonstrate the power of visualization in conveying complex information effectively.The comparison reveals the importance of clear iconography and consistent color palettes in creating impactful visuals. The key takeaway is that the most effective infographics are those that prioritize clarity and conciseness.
Illustrative Images for Each Step
- Step 1: Acknowledgment and Acceptance: An image of a person looking introspectively in a mirror, with a thoughtful expression, can effectively convey self-awareness. The image should be simple, yet impactful.
- Step 2: Understanding the Root Cause: A close-up image of a person analyzing a problem, possibly with a piece of paper displaying the issue, or an image of a puzzle with missing pieces, signifying the need to uncover the core issues. This visual should communicate the investigative nature of the process.
- Step 3: Developing Strategies for Improvement: A person actively engaged in a project, such as working on a computer, planning, or creating a checklist, is appropriate to depict this stage. The image should convey a sense of purpose and proactive action.
- Step 4: Illustrative Examples: An image of a person confidently accomplishing a task previously associated with the weakness, showcasing progress and overcoming the hurdle, is appropriate. The image should inspire and show a successful transformation.
Closing Notes
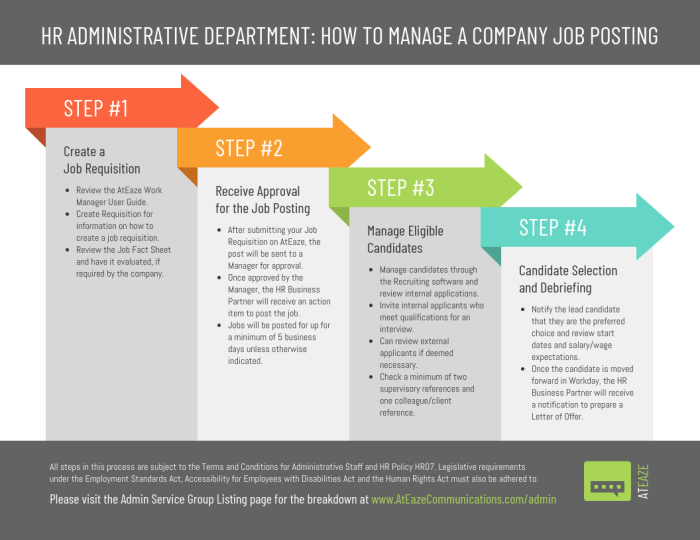
Ultimately, the 4 step process to overcome any weakness empowers you to take control of your personal and professional growth. By understanding the process and applying the strategies presented, you’ll not only overcome specific weaknesses but also develop a more robust and resilient approach to personal development. This journey isn’t just about fixing problems, it’s about building a stronger, more empowered version of yourself.