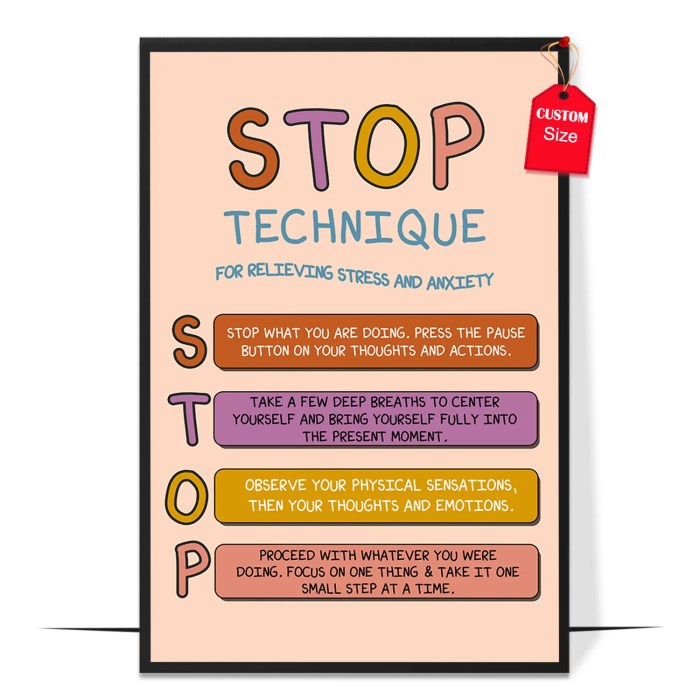
How to stop procrastinating now? This isn’t just about time management; it’s about unlocking your potential and feeling empowered. Procrastination is a common struggle, but understanding its roots and implementing effective strategies can dramatically improve your productivity and well-being. This comprehensive guide will walk you through identifying your procrastination style, implementing immediate action strategies, and building long-term solutions to banish procrastination from your life.
We’ll explore the psychology behind procrastination, from understanding different types to recognizing your personal triggers. We’ll equip you with practical tools and techniques, including self-assessments, actionable steps, and even productivity tools to finally conquer procrastination.
Understanding Procrastination
Procrastination, a seemingly simple act of delaying tasks, often has deep roots in complex psychological and behavioral patterns. It’s not merely laziness; rather, it’s a multifaceted issue affecting productivity and well-being. Understanding the various types, triggers, and underlying factors is crucial to overcoming this habit and fostering better time management.Procrastination isn’t a singular entity but a spectrum of behaviors with differing motivations and consequences.
Recognizing these nuances is the first step towards developing effective strategies to combat it.
Types of Procrastination
Different types of procrastination stem from various motivations and psychological factors. Understanding these types helps tailor strategies for overcoming each.
- Avoidance Procrastination: This type stems from a conscious or unconscious desire to avoid the task itself. The task might be perceived as unpleasant, difficult, or overwhelming. Fear of failure or the pressure of meeting expectations are frequent contributing factors.
- Perfectionism-Driven Procrastination: Perfectionists often delay tasks because they strive for unattainable standards of excellence. This can lead to a cycle of inaction, as the perceived need for flawlessness paralyzes them.
- Decisional Procrastination: This involves the delay of tasks requiring a choice or decision. Overwhelm with numerous possibilities, fear of making the wrong choice, or an inability to evaluate options effectively contribute to this type.
- Procrastination due to lack of motivation: A lack of intrinsic motivation or the absence of interest in the task often leads to postponement. The lack of perceived value or meaning in the task is a key element.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Procrastination
Several psychological factors influence procrastination. These range from personality traits to learned behaviors.
- Low self-efficacy: Individuals with low self-efficacy often believe they lack the ability to successfully complete a task. This perceived inadequacy can lead to avoidance and postponement.
- Fear of failure: The anticipation of negative outcomes or the fear of not meeting expectations can significantly contribute to procrastination. This fear often manifests as anxiety or self-doubt.
- Perfectionism: As mentioned previously, the relentless pursuit of perfection can lead to procrastination. The perceived need for flawless execution can hinder progress and lead to avoidance.
- Impulsivity and poor time management skills: Individuals with impulsive tendencies may struggle with prioritizing tasks and allocating time effectively. This can result in the prioritization of immediate gratification over long-term goals.
Common Triggers and Situations
Various triggers and situations can precipitate procrastination. Identifying these triggers can be instrumental in developing preventative strategies.
- Overwhelmed by workload: A large or overwhelming amount of tasks can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed. This often results in procrastination as an attempt to manage the perceived pressure.
- Lack of clarity or direction: When tasks lack clear instructions or a defined path to completion, it can be difficult to initiate action. This uncertainty can often lead to postponement.
- External pressures and distractions: Distractions such as social media, emails, or other external demands can interrupt focus and lead to procrastination.
- Boredom or lack of interest: Tasks that are perceived as uninteresting or mundane can be easily postponed. A lack of perceived intrinsic value often leads to avoidance.
Negative Impacts of Procrastination
Procrastination has far-reaching consequences, affecting not only productivity but also overall well-being.
- Reduced productivity: Procrastination leads to inefficient task completion and delays, reducing overall productivity.
- Increased stress and anxiety: The anticipation of deadlines and the pressure to complete tasks can heighten stress and anxiety levels.
- Lowered self-esteem: Repeated procrastination can lead to feelings of inadequacy and a decrease in self-esteem.
- Negative impact on relationships: Delayed responsibilities and commitments can strain relationships and create conflicts.
Difference between Procrastination and Time Management Issues
While procrastination is often associated with poor time management, they are distinct concepts.
- Procrastination focuses on avoiding or delaying tasks, often due to psychological factors. Time management issues refer to problems with planning, prioritizing, and scheduling tasks efficiently.
Identifying Your Procrastination Style
Procrastination is a complex behavior, and understanding its nuances is crucial to overcoming it. Different individuals procrastinate for different reasons, and recognizing your personal procrastination style can be the first step towards developing effective strategies for change. Identifying your style involves recognizing the specific triggers, patterns, and accompanying emotions that lead to procrastination.Understanding your procrastination style isn’t about labeling yourself; it’s about gaining insights into your behavior.
This self-awareness can empower you to tailor your approach to managing tasks and achieving goals effectively. The following sections will guide you through a self-assessment process to help you understand your unique procrastination patterns.
Procrastination Style Self-Assessment Questionnaire
This questionnaire is designed to help you identify potential patterns in your procrastination. Answer honestly to gain the most accurate insights. Each question is designed to probe different aspects of your procrastination tendencies.
- Do you tend to put off tasks until the last minute, even when you know you have plenty of time?
- Do you experience anxiety or stress when facing deadlines?
- Do you find yourself avoiding tasks that require sustained effort or concentration?
- Do you experience feelings of guilt or regret after procrastinating?
- Do you have a tendency to focus on tasks that are more enjoyable or easier to complete, even if they are not the most important?
- Do you frequently underestimate the time required to complete a task?
- Do you often feel overwhelmed by large tasks or projects?
- Do you have a history of procrastination in school, work, or personal life?
- Do you experience a sense of relief or a temporary escape from stress after putting off a task?
Comparison of Procrastination Types
Different individuals exhibit varying procrastination styles. This table highlights some common types and their distinguishing characteristics.
| Procrastination Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Perfectionist | Driven by a desire for flawlessness, perfectionists often delay tasks due to fear of not meeting their unrealistic standards. | A student postpones writing a paper because they believe it won’t be perfect enough. |
| Fear-based | Procrastinators driven by fear often avoid tasks that evoke anxiety, like public speaking or presentations. | An employee avoids giving a presentation to colleagues due to a fear of negative feedback. |
| Impulsive | These individuals are easily distracted and tend to switch between tasks, making it difficult to focus on one task at a time. | A student frequently shifts between different activities, hindering progress on their assignments. |
| Overwhelmed | Large tasks and projects seem overwhelming, making the task feel impossible and prompting avoidance. | A project manager delays a large project due to the complexity and number of elements. |
The Procrastination Cycle
Understanding the procrastination cycle is crucial to breaking the pattern. The cycle involves a sequence of events that contribute to delaying tasks.
- A task is perceived as overwhelming or unpleasant.
- Anxiety and fear about the task arise.
- The individual avoids the task, often finding temporary relief.
- Guilt and regret emerge after the avoidance.
- The individual is likely to repeat the cycle with future tasks.
Procrastination and Task/Subject Connection, How to stop procrastinating now
Procrastination is often linked to specific tasks or subjects. This connection can stem from factors like perceived difficulty, perceived lack of interest, or past negative experiences.
- Tasks requiring sustained effort or concentration are frequently avoided.
- Subjects perceived as challenging or uninteresting can trigger procrastination.
- Tasks associated with negative past experiences might elicit avoidance behavior.
Common Procrastination Techniques and Their Impact
Various techniques are used to postpone tasks. Recognizing these techniques and their consequences can be helpful in breaking the cycle.
- Distraction: Engaging in non-essential activities to avoid the task. This can lead to a sense of accomplishment from completing a side task but ultimately hinder progress on the intended one.
- Perfectionism: Setting excessively high standards for a task. This can create an environment of fear and avoidance, leading to inaction.
- Overthinking: Excessive analysis of the task can paralyze the individual and prevent them from starting.
Immediate Action Strategies
Breaking free from procrastination requires more than just understanding its root causes. Effective strategies for immediate action are crucial for interrupting the cycle and achieving your goals. These techniques focus on practical steps to get started, regardless of your current mental state.Effective strategies for immediate action involve techniques for interrupting the procrastination cycle. This is achieved through the implementation of manageable steps, prioritized tasks, and realistic deadlines.
These practical steps are designed to help you take the first step, no matter how small.
So, you’re struggling to stop procrastinating? Sometimes, the key isn’t just brute force, but finding a deeper connection with what you do. Consider this: an unexpected and effective way to find your true calling, like identifying what truly ignites your passion, might just unlock the productivity you’re searching for. By discovering that hidden drive, an unexpected and effective way to find your true calling might help you focus on tasks with renewed energy, making it easier to stop procrastinating now.
This deeper understanding could be the missing link you need to conquer that to-do list.
Interrupting Procrastination Cycles
Procrastination often stems from an overwhelming feeling of needing to tackle a large task. Immediate action strategies aim to break down these intimidating tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. This approach fosters a sense of accomplishment and reduces the perceived difficulty, making it easier to initiate action.
Breaking Down Overwhelming Tasks
Breaking down large tasks is a fundamental technique for managing procrastination. Instead of feeling burdened by the entirety of a project, visualize it as a series of smaller, more achievable steps. For example, if writing a 10-page report feels daunting, create smaller tasks such as researching the topic, outlining the key points, and writing a first draft of each section.
- Identify the task’s component parts. Detailed planning and dividing a project into distinct segments helps in creating an actionable strategy.
- Estimate the time needed for each segment. Realistic time estimations help in creating a realistic schedule and prevent underestimation or overestimation.
- Prioritize tasks within each segment. This enables focusing on the most crucial aspects first, leading to faster progress and a greater sense of accomplishment.
Prioritizing Tasks and Creating Realistic Deadlines
Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic deadlines are vital to maintaining momentum and preventing procrastination. A prioritized list helps you focus on the most important items first. Setting realistic deadlines avoids feeling overwhelmed by tight schedules and allows for flexibility.
- Use the Eisenhower Matrix (Urgent/Important). This method categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance, allowing you to prioritize effectively.
- Set achievable deadlines. Avoid overly ambitious deadlines that lead to stress and decreased motivation. Break down large tasks into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks with their own deadlines.
- Consider your energy levels. Schedule tasks that require more focus or concentration for times when you’re feeling most productive.
Quick-Fix Strategies for Dealing with Procrastination in the Moment
These strategies are designed to combat procrastination when it arises unexpectedly. They provide immediate methods to overcome the urge to postpone.
- The 2-minute rule. If a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately.
- The Pomodoro Technique. Work in focused intervals (e.g., 25 minutes) with short breaks in between to maintain concentration.
- The “Just Start” approach. Sometimes, the most effective way to overcome procrastination is to simply begin the task, even if it’s just for a few minutes.
Immediate Action Methods and Success Rates
While precise success rates are difficult to quantify, the effectiveness of these methods depends heavily on individual circumstances and consistency. The table below offers a general overview.
| Method | Description | Success Rate (General Estimation) |
|---|---|---|
| 2-Minute Rule | Complete tasks that take less than 2 minutes immediately. | High (Often leads to a sense of accomplishment and momentum) |
| Pomodoro Technique | Work in focused intervals with short breaks. | Moderate to High (Improves focus and reduces mental fatigue) |
| “Just Start” Approach | Begin the task, even if it’s for a short period. | Moderate to High (Helps overcome initial inertia) |
Long-Term Solutions for Preventing Procrastination
Overcoming procrastination isn’t a one-time fix; it’s a journey of developing sustainable habits and strategies. Long-term solutions focus on building a framework that supports consistent productivity and reduces the temptation to delay tasks. This approach emphasizes proactive planning, effective time management, and nurturing a positive mindset for sustained success.Procrastination often stems from a lack of structure and a disconnect between goals and daily actions.
Addressing this requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing planning, time management, consistent routines, self-discipline, and a supportive environment. These elements work together to create a positive feedback loop that encourages continued productivity and reduces the allure of procrastination.
Planning and Time Management
Effective planning and time management are crucial for preventing procrastination. A well-structured plan provides a clear roadmap for achieving goals, breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. This allows for a sense of progress and accomplishment, which is often lacking when faced with overwhelming tasks. This clarity of purpose counteracts the feeling of being overwhelmed, a major contributor to procrastination.
Effective Time Management Techniques
Implementing specific time management techniques is key to translating plans into action. Techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, time blocking, and the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important) can help allocate time effectively. The Pomodoro Technique, for example, involves working in focused bursts with short breaks, promoting concentration and preventing burnout. Time blocking involves scheduling specific time slots for particular tasks, ensuring dedicated attention to each activity.
The Eisenhower Matrix prioritizes tasks by urgency and importance, allowing you to focus on what truly matters.
Building Consistent Habits and Routines
Establishing consistent habits and routines is vital for long-term productivity. Routines create a predictable structure, making it easier to integrate tasks into your daily life without conscious effort. Consistency builds momentum, and momentum is a powerful antidote to procrastination. This consistency can range from daily workout schedules to specific study times, creating a sense of structure that anticipates and prevents procrastination.
Improving Self-Discipline and Motivation
Self-discipline and motivation are key components of overcoming procrastination. Developing self-discipline involves creating a strong sense of accountability, recognizing personal values, and maintaining focus. Motivational strategies, such as setting achievable goals, rewarding progress, and celebrating accomplishments, help maintain the drive necessary to stay on track. For example, breaking down a large project into smaller, manageable tasks with clear milestones provides a framework for measuring progress and reinforces motivation.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment fosters productivity and minimizes distractions. A dedicated workspace, free from interruptions, can significantly impact productivity. Minimizing distractions, such as social media notifications or excessive noise, creates a more focused environment. Furthermore, having a support system, whether it’s a study buddy or a mentor, can provide encouragement and accountability, promoting motivation and consistency. A supportive environment can create an atmosphere of encouragement, allowing for sustained effort and reducing the temptation to procrastinate.
Overcoming Specific Procrastination Triggers: How To Stop Procrastinating Now
Procrastination is a complex behavior often rooted in a multitude of underlying factors. Understanding these triggers is crucial to developing effective strategies for overcoming this habit. Identifying and addressing these triggers is the first step in breaking free from the cycle of procrastination. This section dives into common triggers, the role of distractions, the link between perfectionism and procrastination, and how to manage related anxiety and stress.Perfectionism often fuels procrastination.
The fear of not meeting an impossibly high standard can paralyze individuals, leading them to avoid tasks altogether. This avoidance, in turn, exacerbates feelings of inadequacy and anxiety, creating a vicious cycle. By recognizing this connection, individuals can start to reframe their expectations and adopt a more realistic approach to achieving goals.
Common Procrastination Triggers
Procrastination is frequently triggered by a variety of factors, ranging from environmental distractions to personal anxieties. Understanding these triggers allows for targeted interventions to mitigate their impact. Common triggers include overwhelming tasks, fear of failure, and negative self-talk.
- Overwhelming Tasks: Large, complex projects can feel daunting, leading to avoidance. Breaking down these tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make them less intimidating and increase motivation.
- Fear of Failure: The fear of not meeting expectations or failing can paralyze individuals. Reframing this fear into a learning opportunity and acknowledging that mistakes are part of the process can alleviate the anxiety.
- Negative Self-Talk: Internal criticism and self-doubt can significantly contribute to procrastination. Challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with positive affirmations can help build self-confidence and motivation.
Distractions and Procrastination
Distractions are significant contributors to procrastination. From social media notifications to tempting side activities, our modern world is filled with constant interruptions. Developing strategies to minimize distractions is crucial for effective task completion.
- Social Media: Limiting social media usage or creating dedicated blocks of time for checking these platforms can help minimize their distracting influence.
- Notifications: Turning off notifications on devices or using website blockers can prevent interruptions and maintain focus.
- Environmental Clutter: Creating a dedicated workspace free from distractions can enhance concentration and productivity. A tidy and organized environment can significantly reduce procrastination.
Perfectionism and Procrastination
Perfectionism often acts as a powerful procrastination trigger. The fear of not meeting an impossibly high standard can lead to avoidance. Recognizing and challenging these perfectionistic tendencies is crucial for breaking free from the cycle. A key strategy is to set realistic expectations and accept that imperfections are inevitable.
Managing Anxiety and Stress Related to Procrastination
Anxiety and stress related to procrastination can create a vicious cycle. Procrastination often leads to heightened anxiety and stress, which, in turn, further fuels procrastination. Implementing relaxation techniques and stress-reduction strategies can significantly mitigate these negative feelings.
Stopping procrastination requires a proactive approach. Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and prioritize them. For example, if you’re thinking about a real estate investment, consider factors like location, market trends, and potential returns, as discussed in this helpful guide on 4 factors consider before investing real estate. Once you’ve got a plan, you’re much less likely to put things off.
Staying organized and focused on your goals is key to overcoming procrastination.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness exercises and meditation practices can help manage anxiety and stress, promoting a sense of calm and focus.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple deep breathing techniques can quickly calm the nervous system, reducing feelings of anxiety and stress.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and can reduce stress levels.
Methods to Tackle Specific Procrastination Triggers
Addressing specific procrastination triggers requires tailored strategies. These strategies range from task organization to mindfulness techniques. A key aspect is to understand which triggers are most relevant to individual circumstances.
- Task Decomposition: Breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can reduce feelings of overwhelm and increase motivation.
- Time Management Techniques: Employing time management strategies such as the Pomodoro Technique or time blocking can help structure work and minimize procrastination.
- Positive Self-Talk: Replacing negative self-talk with positive affirmations can build confidence and reduce self-doubt.
Building Habits for Consistent Productivity
Overcoming procrastination isn’t a one-time fix; it’s a journey of building sustainable habits. This involves understanding your natural rhythms and aligning your daily routines with your personal productivity peak times. Effective habits, like consistent exercise or a well-structured day, create a foundation for sustained productivity. This approach is more effective than sporadic bursts of intense effort, which often lead to burnout and a renewed cycle of procrastination.Creating a consistent productive routine is not about rigidity, but about structure and flexibility.
A structured daily routine allows you to integrate tasks seamlessly into your day, avoiding the feeling of being overwhelmed or scattered. It’s about creating a framework that supports your goals and fosters a sense of accomplishment. Flexibility allows you to adapt to unexpected events and maintain a positive attitude, even when facing setbacks.
Strategies for Building Productive Habits
Establishing productive habits requires a conscious effort to integrate new routines into your daily life. This includes identifying tasks you consistently put off and proactively scheduling time for them. A key aspect of habit formation is consistency. Consistency is more important than intensity, as long-term, consistent effort is more likely to yield positive results.
- Identify your peak productivity times: Pay attention to when you feel most alert and focused. This may vary depending on the task and your individual circadian rhythm. Schedule demanding tasks for these periods to maximize efficiency.
- Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps: This prevents feeling overwhelmed and provides a sense of accomplishment with each completed step. For example, instead of thinking “write a 10-page report,” think “write one page of the report every hour.” This makes the task seem less daunting.
- Use a timer or productivity app: These tools can help you stay on track and avoid distractions. Set specific time limits for tasks and stick to them as closely as possible. This can be incredibly helpful in managing your time.
- Establish a dedicated workspace: Having a designated area for work can signal to your brain that it’s time to focus and minimize distractions.
Creating a Daily Productivity Plan
A well-structured daily plan provides a roadmap for your day, making it easier to stay on track and avoid procrastination.
- Prioritize tasks: Identify the most important and urgent tasks and schedule them for times when you are most productive. Use methods like the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important) to categorize tasks.
- Schedule buffer time: Allocate time for unexpected events or interruptions. This prevents feeling rushed and allows for flexibility in your schedule.
- Include breaks: Breaks are crucial for maintaining focus and preventing burnout. Short breaks throughout the day can help maintain your energy levels and enhance productivity.
- Review and adjust: Regularly review your daily plan and adjust it as needed to accommodate changing priorities or circumstances. Flexibility is key.
Importance of Self-Care
Self-care is not a luxury; it’s a necessity for maintaining consistent productivity. Taking care of your physical and mental well-being reduces stress and enhances your ability to focus and manage tasks effectively.
- Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to ensure optimal cognitive function.
- Balanced diet: Nourish your body with healthy foods to provide sustained energy throughout the day.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity reduces stress and improves mood, contributing to better focus and concentration.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practice mindfulness exercises like meditation to reduce stress and promote mental clarity.
Celebrating Accomplishments
Celebrating your accomplishments, no matter how small, is vital for maintaining motivation. Acknowledging your progress reinforces positive behaviors and helps you stay on track.
- Reward yourself: Treat yourself to something enjoyable after completing a significant task or reaching a goal. This could be anything from a short break to a small indulgence.
- Acknowledge your progress: Take time to reflect on what you’ve achieved and appreciate your efforts. Keep a journal or use a digital tool to track your accomplishments.
Visual Daily Planner Template
A visually appealing and organized daily planner can be a powerful tool for managing your time effectively. Here’s a simplified example:
| Date | Time | Task | Priority | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2024 | 8:00 AM – 9:00 AM | Morning Exercise | High | Completed |
| October 26, 2024 | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM | Work on Project Report | High | In Progress |
This template allows you to visually track your tasks, priorities, and progress. Customize it with your own colors, fonts, and visual elements to create a planner that works best for you.
Conquering procrastination requires a shift in mindset. One way to get unstuck is to analyze your habits and identify what triggers your delays. Interestingly, understanding the traits of people with mentally strong parents, as detailed in this article on 15 things people who have mentally strong parents understand , often reveals key strategies for overcoming procrastination.
Ultimately, breaking the cycle of procrastination hinges on self-awareness and a proactive approach to tackling tasks.
Tools and Resources for Managing Procrastination
Overcoming procrastination isn’t just about changing habits; it’s about equipping yourself with the right tools and resources. This section delves into practical strategies, from productivity apps to visualization techniques, to empower you to take control and achieve your goals. Choosing the right tools can significantly enhance your ability to stay focused and productive.Understanding that procrastination is a complex issue, the following resources and tools offer multifaceted support for addressing it.
Utilizing these tools can help you identify patterns, manage time effectively, and build the necessary discipline to achieve your goals.
Productivity Apps and Software
Effective productivity apps and software can streamline your workflow and combat procrastination by providing structure and motivation. These tools offer a range of features that can help you organize tasks, track progress, and manage time effectively.
- Todoist, Asana, Trello: These task management apps allow you to create lists, assign deadlines, and collaborate with others on projects. Visual representations of tasks and progress can enhance engagement and motivation.
- Forest, Freedom, Cold Turkey: These apps block distracting websites and apps, creating focused work environments. They can be especially helpful for individuals who struggle with internet distractions.
- Toggl Track, Clockify: These time-tracking tools help you understand how you spend your time. This awareness can reveal patterns of procrastination and help you allocate time more effectively.
Digital Calendar for Scheduling and Task Management
A digital calendar is a powerful tool for managing tasks and schedules. It provides a visual overview of your commitments, deadlines, and appointments, helping you stay organized and avoid missing important events.
- Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar, Apple Calendar: These calendars allow you to schedule appointments, set reminders, and create recurring events. Using color-coding and sub-calendars can further improve organization and clarity. You can create daily, weekly, and monthly views, providing a comprehensive overview of your schedule.
- Integration with Task Management Apps: Linking your calendar with task management apps allows you to automatically schedule tasks based on deadlines and priorities. This integration streamlines your workflow and reduces the chance of forgetting or postponing tasks.
Visualization and Affirmations for Productivity
Visualization and affirmations can be powerful tools for improving productivity and combating procrastination. By visualizing yourself achieving your goals and reinforcing positive affirmations, you can create a mental framework conducive to focused work.
- Visualization Techniques: Imagine yourself successfully completing a task or project. Focus on the feeling of accomplishment and the positive outcomes. This mental rehearsal can increase your confidence and reduce procrastination.
- Affirmations: Repeat positive affirmations related to productivity, such as “I am focused and productive,” or “I can complete this task efficiently.” This reinforces positive self-talk and promotes a more proactive mindset.
Productivity Tool Comparison
| Tool | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Todoist | Excellent task management, clear organization, collaboration features. | Can be overwhelming for some users due to its extensive features. |
| Forest | Effective at reducing distractions, promotes focused work sessions. | Limited functionality compared to comprehensive task management apps. |
| Google Calendar | User-friendly, integrates with other Google services, allows for various scheduling options. | May require more setup for complex scheduling needs. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, stopping procrastination isn’t a quick fix; it’s a journey of self-discovery and consistent effort. By understanding your procrastination style, implementing immediate action strategies, and building long-term solutions, you can reclaim control of your time and unlock your full potential. This guide provides a roadmap for lasting change, empowering you to overcome procrastination and embrace a more productive and fulfilling life.
Ready to start? Let’s dive in!