Leadership vs management is one better than the other – a question that’s been debated for ages. Are they fundamentally different, or just variations on the same theme? This exploration delves into the nuances of leadership and management styles, examining their characteristics, approaches, and impact on organizational performance. We’ll unpack different leadership styles, from transformational to autocratic, and contrast them with various management approaches, from scientific management to contingency management.
We’ll also explore real-world examples to understand how these roles intertwine and impact success.
The discussion will cover how leadership and management skills can be developed and how they contribute to an organization’s culture and employee engagement. We’ll see how successful leaders and managers adapt their styles to various situations and challenges, ultimately contributing to a more effective and thriving workplace.
Defining Leadership and Management
Leadership and management are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts with different focuses and approaches. Understanding their nuances is crucial for effective organizational functioning. While both contribute to achieving goals, their roles and responsibilities differ significantly. This section delves into the specific definitions, highlighting the key characteristics of each, and contrasting their roles in an organizational setting.Effective leaders inspire and motivate individuals, while managers focus on organizing and directing resources.
A successful organization requires both, each playing a vital role in achieving its objectives.
Leadership Defined
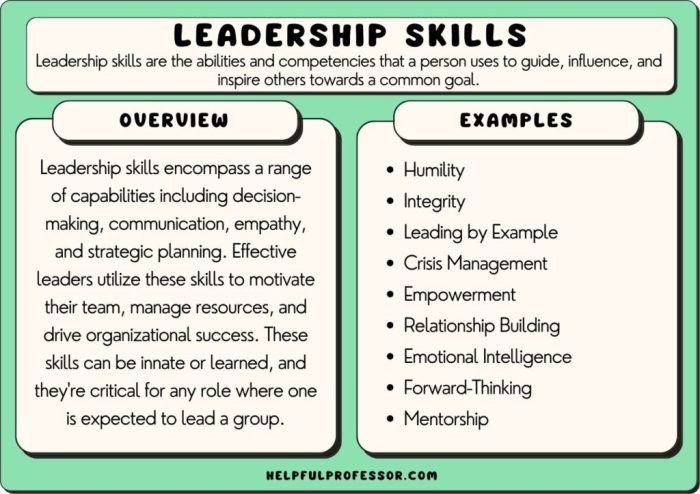
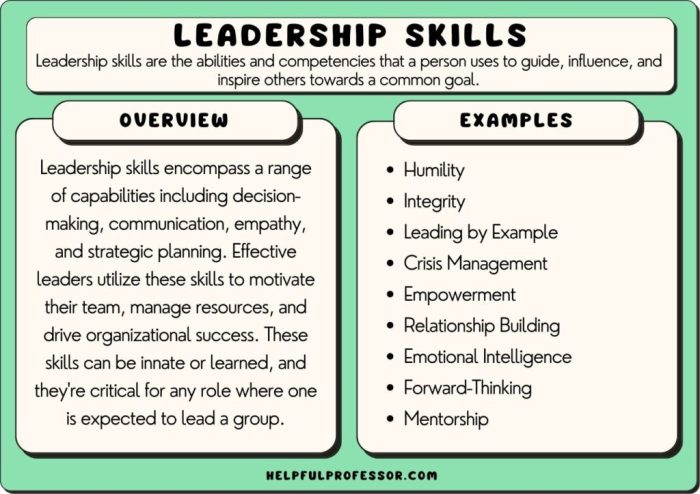
Leadership is the art of influencing and inspiring others to achieve a common goal. It’s about fostering a shared vision, motivating individuals, and empowering them to contribute their best. A core characteristic of effective leaders is their ability to inspire trust and commitment. They demonstrate strong values, ethical conduct, and a proactive approach to problem-solving.
Management Defined
Management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling resources to achieve organizational objectives. Effective managers are proficient in allocating resources, setting clear expectations, and ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently. They focus on the practical aspects of running an organization, like budget management, resource allocation, and operational efficiency.
Comparing and Contrasting Leadership and Management Roles
Leaders and managers both play critical roles in an organization. Leaders inspire and motivate individuals, while managers oversee the day-to-day operations. Leaders focus on the “why” behind the work, while managers focus on the “how.” Leaders are often visionary and future-oriented, whereas managers are more concerned with current operations and maintaining stability.
Differences in Leadership and Management Styles
Leadership styles vary significantly, ranging from autocratic to democratic to laissez-faire. Each style has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the most effective style often depends on the specific situation and the individuals involved. Management styles, conversely, often revolve around maintaining structure, enforcing policies, and ensuring procedures are followed. A key distinction lies in the level of influence and motivation.
Leadership vs. Management Characteristics
| Leadership Characteristics | Management Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Visionary | Results-oriented |
| Inspirational | Organized |
| Motivational | Efficient |
| Future-focused | Present-focused |
| Empowering | Controlling |
| Influential | Directive |
| Strategic | Operational |
| Risk-taking | Risk-averse |
| Adaptable | Predictable |
| Creative | Systematic |
Leadership Styles
Leadership styles significantly impact team dynamics and organizational success. Understanding the diverse approaches leaders employ allows for a more nuanced appreciation of how various leadership models can be implemented and adapted to specific situations. Different leadership styles resonate with varying personalities and organizational cultures, making the choice of style a crucial element in effective management.Effective leaders are often adaptable, recognizing that a single style may not be optimal in every circumstance.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various styles, leaders can strategically adjust their approach to achieve desired outcomes and motivate their teams.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams to achieve extraordinary results by fostering a shared vision and empowering individuals. They focus on the big picture, encouraging innovation and creativity while maintaining a strong ethical compass.Transformational leaders often act as role models, exhibiting high standards of integrity and commitment. Their enthusiasm and passion are contagious, creating a positive and inspiring work environment.
A transformational leader can inspire individuals to go above and beyond their normal duties.Examples of transformational leaders include Martin Luther King Jr., who inspired a generation through his powerful speeches and commitment to equality; and Oprah Winfrey, who used her platform to empower individuals through mentorship and philanthropy.
Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership focuses on clear expectations, rewards, and consequences. Leaders in this style emphasize performance, setting clear goals and providing incentives for achieving them. This approach can be highly effective in structured environments where efficiency and productivity are paramount.Strengths of this style lie in its clear structure and accountability. It can be particularly effective in situations requiring quick decisions and immediate results.
Weaknesses can arise when creativity and innovation are stifled, and the focus solely on immediate goals may hinder long-term vision.Examples of leaders who exemplify transactional leadership include many successful business leaders, particularly in industries with a strong emphasis on production or sales.
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership prioritizes the needs of the team and focuses on empowering and developing individuals. These leaders actively listen, provide support, and strive to create an environment where everyone feels valued and empowered.A key strength of servant leadership is its ability to foster collaboration and trust within the team. This approach creates a supportive and encouraging environment where individuals feel comfortable taking risks and contributing their best work.
However, a potential weakness is that a servant leader might sometimes neglect their own needs or priorities in their focus on serving others.Examples of servant leaders include leaders who prioritize employee well-being and actively seek to create a positive and empowering work environment.
Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leadership involves a centralized decision-making process where the leader retains ultimate authority and control. This style can be effective in situations requiring immediate action or where the team lacks experience.Strengths of autocratic leadership lie in its ability to make swift decisions in emergencies or in environments where there is little time for debate. However, it can stifle creativity and innovation as team members may be discouraged from contributing their ideas or perspectives.
This style can be detrimental to morale in the long term.Examples of autocratic leadership can be found in military settings, or in situations where quick and decisive action is essential.
Comparison Table of Leadership Styles
| Leadership Style | Strengths | Weaknesses | Examples | Effectiveness in Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformational | Inspiring, motivating, fosters innovation | Can be time-consuming, may not be suitable for all situations | Martin Luther King Jr., Oprah Winfrey | Projects requiring long-term vision, creativity, and team collaboration |
| Transactional | Clear expectations, efficient, results-oriented | May stifle creativity, can be demotivating if not coupled with other styles | Many successful business leaders | Structured environments requiring quick decisions and measurable results |
| Servant | Empowering, fosters collaboration, trust | Might neglect leader’s own needs, potential slow decision-making | Leaders who prioritize employee well-being | Environments where trust and collaboration are crucial |
| Autocratic | Quick decisions in emergencies, effective in situations with inexperienced teams | Can stifle creativity, demotivate team members | Military leaders | Crises, situations requiring immediate action |
Management Approaches

Different management approaches have shaped organizational structures and practices throughout history. Understanding these approaches, their strengths, and weaknesses, is crucial for effective leadership and management in today’s dynamic business environment. Each approach has a unique impact on employee motivation and productivity, requiring managers to adapt their strategies based on the specific context and needs of their teams.Management approaches are not static; they evolve and adapt to changing circumstances.
Modern organizations often employ a blend of different approaches, drawing on the strengths of each to create a hybrid strategy that best serves their goals. Analyzing these different approaches allows managers to tailor their strategies and maximize organizational efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Scientific Management
Scientific management, pioneered by Frederick Winslow Taylor, emphasizes optimizing work processes through systematic study and standardization. It focuses on improving efficiency by breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable components, which are then analyzed to identify the most effective methods. This approach aims to maximize productivity by ensuring that every task is performed in the most efficient way possible.
Debating whether leadership or management is “better” is a bit like arguing about which shoe fits best. It really depends on the situation and the people involved. Just like setting healthy boundaries, as discussed in this insightful article on important boundaries empaths should set for themselves in a relationship , strong leadership often involves a keen awareness of individual needs and how to best support them.
Ultimately, effective leadership and management often come down to understanding and adapting to the nuances of the people you’re working with.
- Strengths: Scientific management often leads to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity. By standardizing procedures, it can reduce errors and increase output. It can also improve worker safety by identifying and eliminating hazardous tasks or working conditions.
- Weaknesses: A rigid focus on standardization can stifle creativity and innovation. Employees may feel dehumanized by the perceived lack of autonomy. The emphasis on individual task performance can sometimes lead to a neglect of teamwork and collaboration. It may also not be appropriate in situations where the work environment or tasks are constantly changing.
- Impact on Employee Motivation and Productivity: While initial productivity gains are often seen, sustained motivation can be a challenge. If employees feel like their input is not valued or their creativity is stifled, motivation can decrease over time. If workers feel like they are treated as mere cogs in a machine, their motivation may decrease, leading to reduced productivity.
Bureaucratic Management
Bureaucratic management, championed by Max Weber, emphasizes a structured hierarchy, clear division of labor, and formalized rules and procedures. This approach focuses on ensuring consistency and predictability in operations.
- Strengths: Bureaucratic management promotes efficiency and consistency by clearly defining roles and responsibilities. It ensures a level of accountability and reduces ambiguity. It’s particularly effective in large organizations requiring standardized processes.
- Weaknesses: Bureaucracy can be slow and inflexible, hindering responsiveness to changing circumstances. It can stifle creativity and initiative as employees may feel constrained by rigid rules and procedures. Communication can be hindered by the layers of bureaucracy, potentially slowing decision-making.
- Impact on Employee Motivation and Productivity: Clear structure and defined roles can initially enhance productivity. However, if the bureaucracy becomes overly rigid or stifles employee autonomy, motivation and morale can suffer. Employees might feel demoralized by the lack of flexibility or input in decision-making processes.
Contingency Management
Contingency management recognizes that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to management. This approach suggests that the most effective management style depends on the specific circumstances, including the task, the environment, and the people involved. It emphasizes adapting management strategies to fit the unique situation.
- Strengths: Contingency management allows for flexibility and adaptability, making it suitable for dynamic and unpredictable environments. It encourages managers to assess the specific situation and tailor their approach accordingly. This approach fosters creativity and innovation by empowering employees to contribute their unique perspectives and expertise.
- Weaknesses: Implementing contingency management can be complex as it requires managers to constantly assess and adjust their strategies. This approach can sometimes be perceived as lacking structure, potentially leading to inconsistency in decision-making. The emphasis on situational analysis can sometimes make it challenging to establish clear guidelines and procedures.
- Impact on Employee Motivation and Productivity: Contingency management has the potential to boost employee motivation by acknowledging individual needs and tailoring approaches to fit different circumstances. It can foster a sense of ownership and engagement by empowering employees to contribute to problem-solving and decision-making.
Comparison of Leadership and Management Approaches
Leadership approaches often focus on inspiring and motivating employees, fostering a vision, and encouraging collaboration. Management approaches, on the other hand, tend to concentrate on structuring tasks, defining roles, and ensuring processes are followed.
Key Principles of Different Management Approaches
| Management Approach | Key Principles |
|---|---|
| Scientific Management | Standardization, optimization, efficiency, division of labor |
| Bureaucratic Management | Hierarchy, rules, procedures, formalization, consistency |
| Contingency Management | Adaptability, flexibility, situational awareness, tailoring strategies |
Leadership vs. Management in Practice
Leadership and management are often intertwined, but they possess distinct characteristics. Understanding when one is more crucial than the other is vital for effective organizational performance. This section delves into practical applications, highlighting situations where leadership shines, where management is essential, and how both can collaborate to achieve shared goals.Leadership often takes center stage when navigating complex, ambiguous situations.
Management, on the other hand, excels in structured environments requiring consistent execution. Successful organizations recognize the importance of both and create a synergy between them.
Situations Demanding Leadership, Leadership vs management is one better than the other
Effective leadership is paramount in situations where creativity, innovation, and change are necessary. These circumstances demand vision, inspiration, and the ability to motivate individuals toward a shared future.
Debating whether leadership or management is “better” is a bit like arguing about which shoe fits best. It really depends on the context, right? The Lifehack Show episode on hard work and going the extra mile with T.W. Lewis ( the lifehack show hard work and going the extra mile with t w lewis ) highlights how dedication and effort are crucial for success in any role.
Ultimately, a strong leader likely possesses strong management skills, and vice-versa, but both need to be adapted to different situations for maximum impact.
- Crisis Management: When a company faces a sudden and significant challenge, such as a major product recall or a natural disaster, strong leadership is crucial to maintain composure, make quick decisions, and rally the team. A leader guides the team through the crisis, establishing a clear vision and inspiring confidence. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, leaders in healthcare institutions played a pivotal role in coordinating resources, adapting to evolving guidelines, and reassuring patients and staff.
- Organizational Transformation: Initiating major organizational changes, such as merging with another company or implementing a new technology, necessitates a visionary leader who can articulate the benefits of the change, motivate employees to adapt, and navigate the complexities of the transition. A leader fosters a culture of openness and learning, encouraging employees to embrace the new way of working.
- Developing New Products or Services: Introducing innovative products or services requires a leader who can inspire teams to think outside the box, embrace risk, and persevere through setbacks. Leaders guide the exploration of new ideas and support the development of the product from initial concepts to market launch. The Apple Inc. leadership played a critical role in pioneering new technologies and products that transformed the consumer landscape.
Situations Requiring Management
Management skills are essential in maintaining order, efficiency, and consistency within a structured environment. This encompasses routine tasks, resource allocation, and adhering to established procedures.
- Project Implementation: In a project-based environment, management is critical for coordinating resources, tracking progress, and ensuring that tasks are completed on time and within budget. Managers monitor project deliverables, allocate resources, and identify potential roadblocks to keep projects on track. Construction projects, for instance, rely heavily on management to ensure the proper use of materials, adhere to building codes, and maintain safety.
- Maintaining Operations: In established businesses, daily operations rely on efficient management. Managers are responsible for overseeing workflows, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining productivity. In a factory setting, managers ensure that production lines are running smoothly, materials are delivered on time, and quality control measures are implemented.
- Budgeting and Resource Allocation: Managing financial resources and allocating budgets effectively is a core management function. Managers need to understand and utilize financial tools and models to make informed decisions about resource allocation, maximizing the value of available funds. Government agencies, for example, require strong management skills to allocate funds efficiently and effectively.
Effective Collaboration Between Leaders and Managers
Leaders and managers can complement each other by focusing on their unique strengths. Leaders provide vision and direction, while managers ensure the effective execution of strategies.
- Shared Vision: A leader’s vision must be translated into concrete actions and goals by managers. Effective collaboration involves aligning the vision with specific tasks and responsibilities.
- Open Communication: Regular communication between leaders and managers is crucial for maintaining a cohesive approach. Leaders should actively listen to managers’ insights, while managers should communicate potential challenges and suggestions for improvement.
- Delegation and Empowerment: Leaders should empower managers to take ownership of their tasks, fostering a sense of responsibility and promoting autonomy within their teams.
Integrating Management Principles into Leadership Style
Leaders can enhance their effectiveness by incorporating management principles into their leadership approach.
- Focus on Systems and Processes: Leaders should identify key processes and ensure that systems are in place to support the organization’s goals. This will aid in consistency and efficiency.
- Prioritizing Performance Metrics: Leaders should establish clear performance metrics and track progress towards achieving objectives. This creates a measurable framework for success.
- Utilizing Data-Driven Decision Making: Leaders should use data and metrics to inform decisions, promoting accountability and ensuring decisions are supported by evidence.
Overlapping and Distinct Roles of Leaders and Managers
| Organizational Context | Leader’s Role | Manager’s Role |
|---|---|---|
| Start-up | Visionary, strategic thinker, risk-taker | Operational efficiency, resource allocation, process improvement |
| Established Company | Inspiring, change agent, fostering innovation | Execution, maintaining stability, ensuring adherence to procedures |
| Non-profit Organization | Building community, inspiring donors, fostering trust | Fundraising, managing finances, ensuring program effectiveness |
Impact on Organizational Performance
Strong leadership and effective management are the cornerstones of organizational success. They shape the culture, drive employee engagement, and ultimately influence the bottom line. Understanding how these two crucial functions interact is key to unlocking optimal performance and achieving strategic goals.Effective leadership and management, while distinct, are interconnected and essential for organizational success. They influence each other, impacting the overall organizational climate and employee experience.
This interplay translates to tangible improvements in performance indicators and creates a sustainable competitive advantage.
Impact of Strong Leadership on Organizational Success
Leadership, with its focus on vision and strategy, directly impacts an organization’s ability to adapt and thrive in dynamic environments. Transformational leaders inspire and motivate employees to exceed expectations, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration. This results in a higher degree of commitment and a more cohesive workforce, capable of tackling challenges and capitalizing on opportunities. Visionary leadership sets the direction, aligning efforts towards shared goals and fostering a sense of purpose among team members.
This shared vision leads to higher levels of employee engagement and a more robust organizational structure.
Impact of Effective Management on Organizational Efficiency
Effective management is crucial for translating strategic visions into tangible results. Managers, focusing on planning, organizing, and controlling resources, ensure that tasks are completed efficiently and effectively. This translates to optimized workflows, reduced waste, and improved productivity. By establishing clear processes and procedures, managers create a predictable and organized environment where employees can perform their tasks with clarity and focus.
This organized approach directly contributes to the overall efficiency of the organization.
Leadership and Management’s Contribution to Organizational Culture
Both leadership and management contribute significantly to shaping the organizational culture. Leaders define the values and principles that guide the organization, while managers translate these values into daily practices. Leaders inspire the culture, and managers embody it. A positive and productive organizational culture fosters a sense of belonging, encourages collaboration, and promotes a supportive environment. This supportive environment in turn increases employee satisfaction and loyalty.
How Leadership and Management Influence Employee Engagement
Strong leadership and effective management play a vital role in fostering employee engagement. Leaders create a motivating environment by communicating a compelling vision, empowering employees, and recognizing their contributions. Managers ensure that employees have the necessary resources, support, and opportunities to perform at their best. This results in a highly motivated workforce that is more committed to the organization’s goals.
Debating whether leadership or management is “better” is a bit like arguing over which spice is tastier. It really depends on the context. Looking at how teams handle setbacks, though, can offer some fascinating insights. For example, analyzing the strategies of world cup losing teams provides a unique perspective on building resilience and adapting to challenges, as detailed in this article on 12 things world cup losing teams teach success.
Ultimately, both leadership and management skills are crucial for navigating complex situations, and success often comes from a blend of both.
This positive influence leads to higher levels of job satisfaction, productivity, and retention.
Correlation Between Effective Leadership/Management and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| Leadership/Management Attribute | Key Performance Indicator (KPI) | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Visionary Leadership | Market Share Growth | Positive |
| Employee Empowerment | Innovation Rate | Positive |
| Effective Planning & Control | Project Completion Rate | Positive |
| Open Communication | Employee Satisfaction Score | Positive |
| Team Collaboration | Cross-Functional Collaboration | Positive |
| Resource Optimization | Operational Costs | Negative (lower costs = better) |
| High Retention Rates | Reduced Turnover Costs | Positive |
Strong leadership and effective management are crucial for success in any organization. They directly impact key performance indicators, shaping the overall organizational performance and success.
Developing Leadership and Management Skills: Leadership Vs Management Is One Better Than The Other
Cultivating strong leadership and management skills is an ongoing process, not a destination. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for success in today’s dynamic business environment. Effective leaders and managers consistently seek opportunities to enhance their abilities, understand new trends, and refine their approaches. This dedication to personal and professional growth ultimately benefits both the individual and the organization.Developing these skills requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing self-awareness, practical application, and a willingness to learn from experiences, both successes and failures.
This section will explore key methods for honing both leadership and management abilities, along with valuable resources for further growth.
Methods for Developing Leadership Skills
Developing leadership skills involves fostering a deep understanding of oneself and one’s strengths and weaknesses, combined with a proactive approach to learning and growth. This encompasses understanding diverse leadership styles, adapting approaches to various situations, and consistently seeking feedback.
- Self-Assessment and Reflection: Regularly evaluating one’s leadership style, strengths, and areas for improvement is essential. Tools like personality assessments and 360-degree feedback can provide valuable insights. Journaling about leadership experiences and reflecting on successes and challenges is also a powerful method.
- Learning from Successful Leaders: Studying the biographies, strategies, and leadership styles of prominent figures can provide valuable inspiration and practical examples. Observing and learning from mentors within an organization or in different industries can also be insightful.
- Developing Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing one’s own emotions and those of others is critical for effective leadership. Training programs and resources focused on emotional intelligence can greatly improve interpersonal skills and relationship building.
- Active Participation in Leadership Development Programs: Formal leadership programs, workshops, and seminars provide structured learning opportunities, often involving interactive exercises and real-world case studies.
- Seeking Mentorship: A mentor can provide guidance, support, and valuable insights into navigating challenges and making decisions.
Methods for Developing Management Skills
Effective management involves a combination of technical expertise, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking. Developing these skills necessitates consistent practice and a willingness to adapt to different situations.
- Improving Communication Skills: Clear and concise communication is vital for conveying expectations, providing feedback, and motivating teams. Developing active listening skills and different communication styles for various situations is essential.
- Enhancing Decision-Making Abilities: Management often involves complex decisions. Developing frameworks for decision-making, considering various perspectives, and learning from past decisions can improve this critical skill.
- Mastering Delegation and Empowerment: Knowing when and how to delegate effectively is crucial for optimizing team performance and empowering team members. Providing adequate support and constructive feedback are essential components.
- Improving Conflict Resolution Skills: Addressing disagreements and conflicts constructively is an essential part of effective management. Learning mediation and negotiation techniques can be invaluable.
- Continuous Improvement Through Feedback: Actively seeking and incorporating feedback from team members, superiors, and peers can provide valuable insights for improvement and growth.
Resources for Further Learning
Numerous resources are available to support ongoing learning and development in leadership and management. This includes books, articles, online courses, and professional development programs.
- Books: Numerous books offer insights into various leadership and management styles and theories. Examples include “Good to Great” by Jim Collins, “Drive” by Daniel H. Pink, and “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People” by Stephen Covey.
- Articles: Leading business publications frequently feature articles on leadership and management trends, best practices, and case studies.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning offer a wide range of online courses covering leadership and management principles.
- Professional Development Programs: Many organizations offer leadership and management training programs, often tailored to specific industry needs.
Importance of Continuous Learning
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, continuous learning is paramount for leaders and managers. Staying abreast of new trends, adapting to changing technologies, and refining skills ensures that leaders and managers remain effective and relevant. This approach also fosters innovation, adaptability, and an ability to navigate uncertainty.
Case Studies
Diving deeper into the practical application of leadership and management, case studies offer invaluable insights. They provide concrete examples of how leadership principles and management strategies play out in real-world scenarios, allowing us to analyze successes, identify challenges, and ultimately learn from both triumphs and setbacks. This section will explore two case studies, one highlighting a successful leader and another showcasing an effective manager, to illustrate the nuances of their respective roles and the impact on organizational performance.Analyzing real-world examples provides a tangible understanding of how leadership and management principles translate into practice.
Understanding the approaches, successes, and challenges faced by leaders and managers in these contexts enriches our understanding of the dynamic interplay between these roles and their impact on organizational outcomes.
Successful Leader: Jack Welch at GE
Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric (GE), is renowned for his transformational leadership style. His approach focused on fostering a culture of innovation and high performance. Welch implemented strategies like restructuring the organization, empowering employees, and setting ambitious goals. This resulted in significant growth and market share gains for GE during his tenure.
- Welch’s focus on continuous improvement and innovation fostered a culture of constant adaptation and progress within GE.
- His emphasis on employee empowerment enabled employees to take ownership of their work and contribute to the overall success of the company.
- Welch’s emphasis on performance metrics and accountability drove efficiency and productivity across GE’s various divisions.
Effective Manager: Mary Barra at GM
Mary Barra, CEO of General Motors (GM), exemplifies effective management through strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. Her approach emphasizes strong communication, collaboration, and a commitment to safety and sustainability. Under Barra’s leadership, GM has undergone a significant transformation, focusing on product innovation, technological advancements, and environmental responsibility. This has resulted in improved financial performance and enhanced reputation.
- Barra’s emphasis on clear communication and transparency fostered trust and collaboration among employees and stakeholders.
- Her proactive approach to addressing safety concerns within the company demonstrated a commitment to employee well-being and public safety.
- Barra’s focus on sustainability and innovation aligned GM with the evolving needs and expectations of consumers.
Leadership and Management in the Case Studies
Both Welch and Barra demonstrate the interconnectedness of leadership and management. Welch’s transformational leadership style set the strategic direction, while Barra’s management approach ensured the effective implementation of those strategies. Leadership provided the vision and motivation, while management ensured the execution and optimization of resources.
- Leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating individuals to achieve a shared vision, setting the strategic direction for the organization.
- Management focuses on the practical implementation of strategies, ensuring efficient resource allocation and execution of tasks.
Challenges Faced by Leaders and Managers
Leaders and managers in these case studies faced numerous challenges. Welch navigated the complexities of restructuring a large, diverse organization, while Barra dealt with the reputational damage and safety concerns following major incidents. Both leaders had to adapt their approach to overcome these challenges and maintain their companies’ success.
- Resistance to change from employees and stakeholders presented a significant hurdle for both Welch and Barra.
- Maintaining a balance between innovation and risk management was a key challenge for both leaders.
- Adapting to rapid technological advancements and evolving market demands was another key challenge for both leaders.
Adapting Approaches to Overcome Challenges
Welch addressed resistance to change by fostering open communication and involving employees in the decision-making process. Barra proactively addressed safety concerns through rigorous audits and process improvements. Both leaders demonstrated the importance of flexibility and adaptability in responding to the ever-changing business landscape.
Last Word
In conclusion, while leadership and management are distinct, they are not mutually exclusive. Effective organizations recognize the importance of both strong leadership and efficient management. A successful leader often incorporates management principles into their approach, while a skilled manager needs to inspire and motivate their team, showing leadership qualities. Ultimately, the best approach depends on the specific situation and the individuals involved.
This exploration provides a framework for understanding the crucial roles of leadership and management in achieving organizational success.





