8 reasons why children should not use handheld devices frequently: This isn’t about banning technology entirely, but about striking a healthy balance. Excessive handheld device use can have significant, negative impacts on children’s development, health, and well-being. From physical issues to social isolation, the consequences can be far-reaching and detrimental. Let’s delve into the eight key reasons why limiting frequent handheld device use is crucial for a child’s healthy growth.
The constant stimulation and accessibility of handheld devices can lead to a multitude of challenges. Children are spending increasing amounts of time immersed in these digital worlds, often at the expense of crucial physical activities, social interaction, and healthy sleep patterns. This article will explore the various negative impacts of excessive handheld device use on children, providing insights into how these effects can be mitigated and a balanced approach can be established.
Negative Impacts on Physical Health
Excessive handheld device use among children is a growing concern, leading to a range of detrimental physical health effects. These devices, while offering some benefits, often displace crucial physical activities that are essential for healthy development. The sedentary nature of prolonged screen time contributes significantly to the overall negative impact on children’s well-being.
Physical Health Problems Associated with Excessive Handheld Device Use
Prolonged screen time negatively impacts children’s physical health in various ways. It often displaces necessary physical activity, contributing to weight gain and obesity. Furthermore, poor posture and repetitive strain injuries are common consequences of prolonged, improper use of handheld devices. Ultimately, these factors can contribute to chronic health issues later in life.
Examples of Physical Health Problems
- Obesity and Weight Gain: Reduced physical activity, coupled with increased consumption of unhealthy foods often consumed while engaging with devices, leads to a significant increase in weight gain. This can have serious implications for children’s health, increasing the risk of developing obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. For instance, studies have shown a strong correlation between excessive screen time and higher body mass index (BMI) in children.
- Eye Strain and Vision Problems: The close-up nature of handheld devices, coupled with the constant exposure to bright screens, can cause eye strain, headaches, and even nearsightedness. Prolonged screen time can lead to eye fatigue and dry eyes, impacting a child’s overall comfort and academic performance. Children spending significant time on devices often have difficulty maintaining focus, which can be a factor in their eye strain.
- Musculoskeletal Problems: Poor posture, such as hunching over devices, can lead to neck pain, back pain, and other musculoskeletal issues. Repetitive movements, like thumb typing, can also result in carpal tunnel syndrome and other repetitive strain injuries. These issues can limit a child’s physical activity and overall quality of life. For example, children who consistently engage in prolonged gaming sessions without proper posture are more susceptible to developing neck pain and backaches.
Impact on Overall Well-being
The negative physical health effects of excessive handheld device use extend beyond the immediate symptoms. Obesity, for example, can lead to self-esteem issues and social isolation. Eye strain can affect academic performance and concentration. Musculoskeletal problems can hinder physical activities and sports participation. These issues collectively contribute to a decreased quality of life for children.
Children with chronic pain or eye strain often experience decreased motivation for other activities and face difficulties in concentrating on schoolwork.
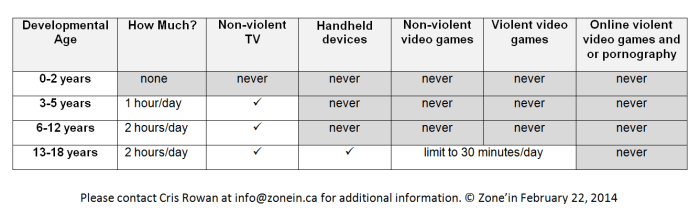
Handheld Device Use by Age Group and Potential Health Implications
| Age Group | Average Daily Handheld Device Use (estimated) | Potential Health Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Preschool (3-5 years) | 1-2 hours | Increased risk of obesity, eye strain, difficulty developing essential motor skills. |
| Elementary School (6-11 years) | 2-3 hours | Increased risk of obesity, eye strain, musculoskeletal problems, and decreased time for physical activities. |
| Middle School (12-14 years) | 3-4 hours | Increased risk of obesity, eye strain, musculoskeletal problems, and potential social isolation. |
| High School (15-18 years) | 4-5+ hours | Increased risk of obesity, eye strain, musculoskeletal problems, potential sleep disturbances, and social isolation. |
Note: These are estimated averages and individual usage can vary significantly. The potential health implications are not exhaustive and may vary based on individual factors and specific device usage patterns.
Solutions to Mitigate Negative Effects
Establishing clear limits on handheld device use, encouraging physical activity, promoting healthy eating habits, and ensuring proper posture during device use can help mitigate these negative impacts. Encouraging outdoor play and other physical activities is vital for counteracting the sedentary nature of screen time. Parents and educators should play a crucial role in guiding children towards a balanced lifestyle that incorporates both digital and physical engagement.
Developmental Delays and Cognitive Issues
Excessive handheld device use in children can significantly impact their cognitive development and overall well-being. The constant stimulation and immediate gratification offered by these devices can sometimes overshadow the crucial developmental processes that occur through exploration, play, and interaction with the physical world. This, in turn, can lead to a range of potential challenges, affecting not only academic performance but also social and emotional growth.The brain develops rapidly during childhood, with critical periods for learning language, problem-solving, and social interaction.
Handheld devices, while offering some educational opportunities, often do not replicate the nuanced learning that happens through real-world experiences. The immediate feedback loops and simplified interactions inherent in many apps can potentially hinder the development of deeper cognitive skills. Children need opportunities to grapple with complex concepts, experiment with different solutions, and learn from their mistakes in a more organic way.
Correlation Between Excessive Use and Developmental Delays
The relationship between excessive handheld device use and potential developmental delays is complex and multifaceted. Studies suggest a correlation, but causality is difficult to definitively establish. The impact is often observed through reduced attention spans, difficulties with sustained concentration, and challenges with executive function skills like planning and problem-solving. These issues can manifest in various ways, from struggles in school to challenges in social interactions.
For example, a child constantly engaged with a device might exhibit decreased interest in exploring their surroundings, interacting with peers, or engaging in imaginative play.
Impact of Different Device Types
Different types of handheld devices can have varying impacts on a child’s cognitive skills. Games with simple mechanics and immediate rewards might offer less cognitive stimulation than games requiring strategic thinking and problem-solving. Educational apps, while potentially beneficial, can also fall short if they don’t encourage active learning and exploration. A child engaging with a tablet solely for watching videos may develop different cognitive skills compared to a child actively using a device to build a virtual model or play a game that involves problem-solving.
While it’s fascinating to see how smartphones are evolving, like in five ways smartphones search smart , it’s crucial to remember the 8 reasons why excessive handheld device use isn’t good for kids. From eye strain to potential social isolation, the downsides are significant. We need to prioritize their well-rounded development and limit screen time to foster healthy habits.
Impact on Social and Emotional Development
Reduced interaction with the physical world can significantly affect a child’s social and emotional development. The constant engagement with virtual interactions can hinder the development of crucial social skills like empathy, perspective-taking, and communication in real-life settings. For instance, a child who spends most of their time interacting with avatars might struggle to understand the nuances of nonverbal communication or develop effective strategies for resolving conflicts in person.
This isolation can lead to difficulties in forming meaningful relationships and understanding emotional responses.
Strategies to Encourage Balanced Development
Promoting a balanced approach to screen time is crucial for fostering healthy development. Limiting screen time to specific, designated periods is a first step. Encouraging activities that stimulate physical interaction, creativity, and social engagement, such as outdoor play, arts and crafts, and interactive games, can create a more well-rounded experience. Parents and educators play a vital role in modeling healthy habits and creating environments that prioritize real-world interactions.
Open discussions about the potential impacts of excessive screen time and strategies for managing it can foster a more mindful approach. Establishing clear rules and expectations around device use, coupled with age-appropriate activities, can greatly assist in mitigating potential negative impacts.
Eye Strain and Vision Problems
Excessive screen time, particularly with handheld devices, can significantly impact a child’s developing eyes. Prolonged exposure to the close-up, focused nature of screens can lead to a range of eye-related issues, impacting not only their physical well-being but also their ability to learn and participate in other activities. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for parents and educators to implement preventative strategies.Excessive screen time puts considerable strain on the eye muscles, especially those responsible for focusing.
Ever wonder why kids are glued to their phones? Well, 8 reasons why children shouldn’t use handheld devices frequently are crucial. Think about it, if you’re looking to improve your life, checking out this list of 20 things you should stop doing now to make your life 50 amazing might help 20 things you should stop doing now make your life 50 amazing.
Ultimately, limiting screen time for kids is vital for healthy development, and those 8 reasons are key to fostering a balanced lifestyle.
This strain, when repeated frequently, can lead to discomfort, headaches, and potentially more serious vision problems. Furthermore, the constant close-up work required for handheld devices often differs from the natural visual tasks children engage in throughout the day, exacerbating the potential for developing eye problems.
Link Between Prolonged Screen Time and Eye Strain
The constant need to focus on a small screen at close range requires significant effort from the eye muscles. This sustained effort can lead to eye fatigue and discomfort, commonly known as eye strain. Children, with their still-developing visual systems, are particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of prolonged screen time. Symptoms of eye strain can include blurry vision, headaches, eye pain, and a feeling of tightness or pressure around the eyes.
The repeated strain over time can contribute to the development of more serious vision problems.
Different Types of Vision Problems
Frequent and prolonged use of handheld devices can contribute to various vision problems in children. One common issue is myopia, often referred to as nearsightedness. Myopia develops when the eye grows too long, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. This makes it difficult to see objects at a distance.
Another potential issue is astigmatism, a condition where the cornea or lens has an irregular shape, preventing light from focusing sharply on the retina. This can lead to blurry vision at all distances. Furthermore, there’s the possibility of developing amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, where one eye doesn’t develop properly. Prolonged screen use can contribute to the development of amblyopia, particularly if the child has a predisposition to the condition or doesn’t have proper eye care.
Finally, children might experience increased susceptibility to dry eye syndrome, a condition characterized by insufficient tear production. This can exacerbate eye strain and discomfort, particularly in children spending significant time on screens.
While there are 8 compelling reasons why children shouldn’t overuse handheld devices, it’s important to remember that fostering a positive mindset, like being proud of accomplishments, can be incredibly beneficial. Being proud can bring a positive force to your life and help kids build resilience and confidence. Ultimately, limiting screen time is key to nurturing well-rounded development and allowing children to explore the vast world around them, instead of being glued to a screen.
Impact of Eye Strain on Focus and Learning
Eye strain can significantly impact a child’s ability to focus and learn. When eyes are strained, the brain struggles to process visual information effectively. This can lead to difficulties in concentrating on tasks, whether in school or during other activities. Blurry vision or discomfort can also lead to decreased motivation and engagement in learning, impacting academic performance.
A child experiencing constant eye strain may find it challenging to follow instructions, participate in class discussions, or complete assignments, thereby impacting their overall academic progress.
Preventative Measures for Eye Strain and Vision Problems
Maintaining a healthy balance between screen time and other activities is crucial. Creating clear screen-time limits is vital. Regular breaks from screens are essential to allow the eye muscles to rest and recover. Following the 20-20-20 rule, which suggests looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes, can be a helpful guideline. Encouraging outdoor activities, which provide natural visual stimulation at different distances, is another important preventative measure.
Ensuring adequate lighting is crucial. Dim or overly bright light can strain the eyes. Maintaining proper distance from the screen is important. Adequate lighting and correct distance from the screen help minimize strain. Regular eye check-ups are also critical.
Regular eye examinations can detect potential vision problems early and provide appropriate intervention.
| Preventative Measure | Details |
|---|---|
| Screen Time Limits | Establish and consistently enforce limits on screen time. |
| Regular Breaks | Encourage regular breaks from screens, especially during prolonged use. |
| 20-20-20 Rule | Follow the 20-20-20 rule to alleviate eye strain. |
| Outdoor Activities | Promote outdoor activities to provide visual stimulation at various distances. |
| Adequate Lighting | Ensure proper lighting conditions to reduce eye strain. |
| Correct Distance | Maintain a suitable distance from the screen to minimize eye strain. |
| Regular Eye Check-ups | Schedule regular eye check-ups to detect and address potential vision problems early. |
Sleep Disturbances and Sleep Disorders
Screen time before bed significantly impacts a child’s sleep quality. The constant stimulation and exposure to bright lights from handheld devices interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to various sleep disturbances and potential disorders. These disruptions can have profound effects on their overall well-being and development.The blue light emitted from screens suppresses the production of melatonin, a hormone crucial for regulating sleep.
This disruption of the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle can result in difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and experiencing a variety of sleep-related issues. Melatonin production is typically triggered by darkness, and exposure to bright light, particularly blue light, can interfere with this process. The intensity and duration of screen time before bed directly correlate with the extent of this disruption.
Impact of Blue Light on Melatonin Production
Children’s brains are particularly sensitive to the effects of blue light. Studies have shown that even short periods of screen time close to bedtime can significantly reduce melatonin levels. This disruption can lead to a cascade of negative consequences on their sleep, impacting their physical and cognitive development. The intensity of the blue light emitted from screens varies, with brighter screens having a more pronounced effect on melatonin suppression.
Strategies to Improve Sleep Hygiene
Establishing consistent sleep routines is vital for children’s well-being. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine that helps children wind down before sleep can promote better sleep quality. Activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music can prepare them for sleep.
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: A regular sleep schedule, including consistent bedtimes and wake-up times, helps regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Consistency is key to improving sleep quality.
- Create a Dark and Quiet Sleep Environment: Minimizing light and noise in the bedroom can create a conducive environment for sleep. Using blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines can be helpful. Darkness cues the body to produce melatonin.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Limiting screen time at least an hour before bedtime is crucial for optimizing sleep. The blue light emitted from screens interferes with melatonin production, leading to difficulties falling asleep.
- Encourage Relaxation Techniques: Relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises or meditation can help children calm their minds and bodies before sleep. These activities can ease anxiety and promote better sleep quality.
- Ensure Adequate Sleep Duration: Children require sufficient sleep for optimal development and functioning. The recommended sleep duration varies based on age, and adhering to these guidelines is important.
Impact of Inconsistent Sleep on Overall Health and Academic Performance
Sleep deprivation negatively impacts various aspects of a child’s well-being. It can affect their mood, concentration, and ability to learn and retain information. Children who do not get enough sleep may exhibit irritability, difficulty concentrating in school, and decreased academic performance.
- Mood and Behavior: Lack of sleep can lead to mood swings, irritability, and behavioral problems in children. This can impact their interactions with peers and their overall emotional well-being.
- Cognitive Function: Sleep is essential for memory consolidation and cognitive function. Children who do not get enough sleep may experience difficulty with learning, concentration, and problem-solving.
- Academic Performance: Insufficient sleep directly affects academic performance. Children who are sleep-deprived may have difficulty concentrating in class, remembering information, and performing well on assignments. This can lead to a decline in grades and overall academic achievement.
Social Isolation and Communication Skills
Excessive screen time can significantly hinder a child’s social and emotional development, leading to a concerning degree of social isolation. Handheld devices, while offering entertainment and connectivity, can inadvertently replace vital face-to-face interactions, crucial for building essential social skills. This detachment from real-world social situations can have lasting consequences on a child’s ability to navigate complex social environments and form meaningful relationships.The digital world, though seemingly inclusive, can ironically isolate children.
Children immersed in the virtual realm may find it challenging to engage with peers in person, potentially leading to decreased confidence and communication skills. They might struggle with non-verbal cues, understanding social dynamics, and participating in collaborative activities. This isolation can manifest in a variety of ways, from reluctance to participate in group activities to difficulty initiating conversations or maintaining friendships.
Impact on Social Skills Development
The frequent use of handheld devices can disrupt the development of crucial social skills. Children learn social cues and appropriate responses through observation and interaction with others in real-life scenarios. Limited face-to-face interactions result in a slower acquisition of these essential skills.
Examples of Hindered Social Skills, 8 reasons why children should not use handheld devices frequently
- Reduced ability to initiate and maintain conversations: Children who spend extensive time on devices may find it challenging to engage in meaningful conversations with peers, as they haven’t practiced these interactions regularly. This can lead to difficulties in understanding social cues and responding appropriately.
- Difficulty interpreting non-verbal cues: Online communication often lacks the richness of non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice. This lack of exposure can lead to misinterpretations and misunderstandings in real-life social situations. For example, a child might misinterpret a friend’s frown as simply a bad mood, failing to recognize the underlying cause.
- Limited experience with collaborative activities: Handheld devices often encourage solitary play. Children might miss opportunities to develop teamwork skills, negotiate, compromise, and resolve conflicts, all of which are essential for successful interactions with peers.
Practical Tips for Fostering Healthy Social Interaction
Encouraging healthy social interaction in children who spend a lot of time on handheld devices requires a proactive approach. Parents and educators play a crucial role in guiding children towards balanced screen time and fostering meaningful social interactions.
- Structured screen time limits: Establishing clear guidelines regarding screen time usage can help children develop a balanced perspective, allowing them to appreciate both digital and real-world experiences.
- Scheduling dedicated face-to-face time: Regularly scheduling activities that require face-to-face interaction, such as family dinners, board game nights, or playdates, can promote social skills development.
- Encouraging participation in extracurricular activities: Joining sports teams, clubs, or community groups allows children to interact with peers in structured environments, fostering essential social skills and teamwork.
Importance of Face-to-Face Interactions
Face-to-face interactions are paramount for social and emotional development. They provide children with opportunities to:
- Develop empathy and understanding: Observing and interacting with others in person allows children to understand diverse perspectives, build empathy, and develop emotional intelligence.
- Build stronger relationships: Face-to-face interactions foster genuine connections and stronger bonds with peers and family members, leading to a more supportive and nurturing environment.
- Improve communication skills: Real-life interactions help children refine communication skills, learn to listen actively, and express themselves effectively in a wide range of social contexts.
Attention Deficit and Focus Issues

The constant barrage of stimuli from handheld devices can significantly impact a child’s ability to focus and sustain attention. The immediate gratification and quick-paced nature of these devices often create a preference for short bursts of engagement, hindering the development of sustained attention. This can translate into difficulties in classroom settings, academic performance, and even social interactions.Frequent handheld device use can lead to a shorter attention span, making it harder for children to concentrate on tasks requiring sustained effort.
The immediate rewards and constant stimulation from screens can train the brain to seek out quick bursts of entertainment, making it challenging to maintain focus on more demanding activities. This is often seen in children who struggle to complete homework assignments, listen attentively during lessons, or engage in activities that require prolonged concentration.
Impact on Concentration
The rapid-fire nature of handheld devices, with their constant notifications and interactive elements, can rewire the brain to prioritize immediate gratification over sustained attention. Children accustomed to this constant stimulation might find it difficult to transition to activities requiring prolonged concentration, like reading, completing complex puzzles, or engaging in meaningful conversations. This can lead to frustration and difficulty in learning and development.
Improving Focus and Attention Span
Developing a child’s focus and attention span requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not about completely eliminating screen time, but rather about establishing healthy boundaries and promoting alternative activities that encourage sustained engagement. A combination of structured routines, mindful activities, and engaging learning experiences can significantly improve a child’s ability to concentrate.
Strategies for Improved Focus
- Establish Clear Routines: Predictable schedules and designated times for screen use can help children regulate their attention and prepare for tasks requiring focused attention. Consistent routines signal the brain that certain times are for specific activities, fostering a sense of order and predictability. For example, a child might have designated screen time only after completing homework and chores.
- Mindfulness Practices: Incorporating mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing exercises or guided meditations, can help children develop self-awareness and control over their attention. These practices help calm the mind and improve the ability to focus on the present moment.
- Engaging Learning Activities: Encourage participation in activities that require sustained attention, such as reading, playing board games, engaging in arts and crafts, or participating in sports. These activities encourage a child to focus on the task at hand, leading to improvements in their attention span.
Comparing Learning Methods
| Learning Method | Description | Impact on Attention Span |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Classroom Setting | Structured learning environment with lectures and group discussions. | Can be challenging for children with shorter attention spans; requires active engagement to maintain focus. |
| Interactive Learning Platforms | Educational games and apps that incorporate interactive elements. | Can initially engage attention but may lead to difficulty sustaining focus on more challenging tasks. |
| Project-Based Learning | Hands-on learning through projects and investigations. | Promotes sustained engagement and exploration, leading to improved focus and problem-solving skills. |
| Outdoor Play and Exploration | Activities like hiking, playing in nature, and participating in sports. | Provides opportunities for focused attention on tasks and challenges, developing problem-solving skills and physical development. |
Cyberbullying and Online Safety Concerns
The digital world, while offering incredible opportunities, also presents unique challenges for children. Handheld devices, with their constant connectivity, expose them to a range of online risks, particularly cyberbullying. Understanding these dangers and equipping children with the tools to navigate them safely is crucial for their well-being and development.Cyberbullying involves the use of electronic communication to harass, threaten, or humiliate another person.
This can take many forms, including sending hurtful messages, posting embarrassing photos or videos, spreading rumors, and creating fake social media profiles. The anonymity and reach of online platforms amplify the potential harm, as cyberbullying can be far more pervasive and difficult to escape than traditional bullying.
Recognizing the Risks of Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying can have devastating consequences for children. It can lead to anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, and even suicidal thoughts. The constant fear of online harassment can significantly impact a child’s ability to concentrate, participate in school activities, and form healthy relationships. Victims may experience feelings of isolation, shame, and helplessness. Cyberbullying is not just about words; it’s about the power dynamics and the ability to inflict harm without direct physical contact.
Educating Children About Online Safety
Teaching children about online safety is paramount. This education should encompass a range of skills, from recognizing and avoiding inappropriate content to understanding the importance of privacy settings and responsible social media use. Children need to learn to identify and report cyberbullying incidents and to seek help when they are being targeted.
Strategies for Parents and Educators
Parents and educators play a vital role in protecting children from cyberbullying. Open communication about online safety is essential. Establish clear rules and expectations for internet use, emphasizing respect, empathy, and responsible behavior. It’s crucial to create a supportive environment where children feel comfortable discussing their online experiences and seeking help if they encounter difficulties. Active monitoring of online activity, while respecting privacy, can also help identify potential issues early on.
Encourage children to block or report cyberbullying incidents.
Resources for Online Safety Support
Numerous resources are available to support children and families in navigating the complexities of online safety. Organizations dedicated to child safety and online well-being offer educational materials, advice, and support programs. Many schools and communities also provide resources to help children and parents understand the risks and develop strategies to prevent and respond to cyberbullying. These resources often include online safety workshops, educational materials, and reporting mechanisms.
- National Center for Missing and Exploited Children: Provides information on internet safety, cyberbullying, and resources for reporting online abuse.
- StopBullying.gov: Offers resources for parents, educators, and children on recognizing and responding to cyberbullying.
- The Cybersmile Foundation: Focuses on online safety education and provides support for children, teens, and parents.
- Local law enforcement agencies: Can offer advice and support for victims of cyberbullying and can investigate reported incidents.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: 8 Reasons Why Children Should Not Use Handheld Devices Frequently
The modern world, with its readily available entertainment options, often encourages a sedentary lifestyle. Children, particularly, are increasingly spending extended periods engaged with handheld devices, often at the expense of physical activity. This shift towards a more sedentary routine has significant implications for their health and well-being, potentially leading to weight gain and obesity.
Handheld devices, while offering various educational and entertainment possibilities, often replace active pursuits like playing outdoors, engaging in sports, or simply exploring their surroundings. The constant screen time limits opportunities for movement and energy expenditure. This lack of physical activity directly contributes to an imbalance in energy expenditure, potentially leading to excess calories being stored as fat, thereby increasing the risk of weight gain and obesity.
It’s a subtle but significant shift that can have long-lasting health consequences.
Relationship Between Handheld Device Use and Increased Sedentary Behavior
The correlation between increased handheld device use and decreased physical activity is undeniable. Children who spend excessive time on screens are often less inclined to participate in physical activities, preferring the passive engagement offered by digital entertainment. This reduced activity level directly contributes to a sedentary lifestyle, limiting opportunities for burning calories and maintaining a healthy weight.
How Increased Sedentary Behavior Contributes to Weight Gain and Obesity
A sedentary lifestyle leads to a lower metabolic rate, meaning the body burns fewer calories at rest. When coupled with a typical diet, this can result in a net energy surplus. This surplus is stored as fat, contributing to weight gain and, over time, obesity. Consider a child who spends hours playing video games instead of playing outside.
This reduced physical activity leads to a decreased calorie expenditure, which, combined with a typical diet, can contribute to weight gain. This pattern can have a detrimental impact on their overall health and well-being, leading to various health complications in the future.
Strategies to Encourage More Physical Activity in Children
Encouraging children to be more physically active requires a multifaceted approach that considers their interests and developmental stage. Creating opportunities for active play and fostering a love for physical activity from a young age are key components of this approach.
- Establish a Routine: Integrating physical activity into daily routines can significantly improve the amount of exercise a child gets. This could include scheduled playtime outdoors, walking to school, or engaging in family sports activities. A structured approach can make physical activity a consistent part of their lives.
- Create Opportunities for Active Play: Designate specific times for outdoor play, organize sports activities, or encourage active games and hobbies like cycling, swimming, or skateboarding. This fosters an appreciation for movement and physical exertion.
- Lead by Example: Children often mimic the behaviors of their parents and caregivers. If adults prioritize physical activity, children are more likely to follow suit. Demonstrate a healthy lifestyle through active participation in sports, walks, or other activities.
- Incorporate Physical Activity into Daily Tasks: Encourage children to walk or cycle instead of taking the car for short distances, take the stairs instead of the elevator, or play active games during breaks or downtime. These small changes can accumulate over time and significantly increase their physical activity levels.
- Encourage Active Hobbies: Encourage children to participate in activities they enjoy, such as dancing, sports, or outdoor games. This fosters a positive association with physical activity, making it a more enjoyable and sustainable part of their lives.
Balancing Screen Time with Physical Activity
Balancing screen time with physical activity is crucial for a child’s overall health and development. It’s essential to establish healthy boundaries and guidelines for screen time and to actively promote physical activity.
“Children need a healthy balance of screen time and physical activity to develop their physical, mental, and social skills effectively.”
The key is to establish clear limits for screen time and create a supportive environment that encourages regular physical activity. This approach helps prevent the negative impacts of excessive screen time and promotes healthy habits for life.
Final Review
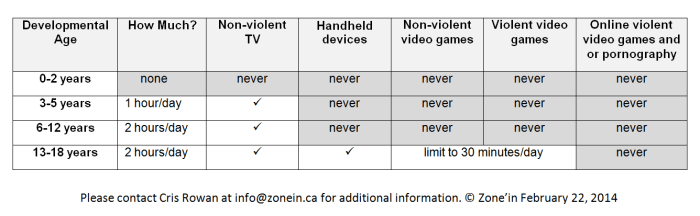
In conclusion, while technology has its place in modern life, limiting excessive handheld device use in children is essential for their overall well-being. By prioritizing physical activity, face-to-face interaction, and sufficient sleep, parents and educators can help children develop into well-rounded individuals. Understanding the multifaceted impacts of frequent screen time is crucial for fostering a healthy balance in their lives.
Let’s encourage a healthy integration of technology, rather than an all-consuming reliance.