10 habits people who can always generate great ideas. Unlocking the secrets to innovative thinking isn’t about some mystical gift, but rather a collection of learnable habits. From cultivating curiosity and proactive information gathering to embracing experimentation and persistence, this exploration reveals the pathways to creative brilliance. Discover how connecting the dots, effective communication, and a problem-solving approach can all contribute to a constant stream of fresh ideas.
This exploration dives deep into 10 specific habits that consistently fuel the creative process. We’ll examine the importance of open-mindedness, proactive information gathering, and the power of connecting seemingly disparate concepts. Discover how experimentation, persistence, and effective communication all play a role in bringing innovative ideas to life.
Curiosity and Open-mindedness
A thirst for knowledge and a willingness to embrace diverse perspectives are crucial for generating innovative ideas. This mindset fosters a constant state of learning, allowing individuals to connect seemingly disparate concepts and develop unique solutions. The ability to question assumptions and explore unfamiliar territories is paramount in a world constantly evolving.Continuous learning and exploration, the cornerstone of innovative thinking, fuels the creative process by expanding one’s knowledge base and broadening their perspectives.
This expanded understanding allows for the identification of new problems, the discovery of novel connections, and the generation of unique solutions. Embracing ambiguity and uncertainty is key to unlocking creativity and fostering the emergence of novel ideas.
The Power of Continuous Learning
A mindset of continuous learning is essential for idea generation. Individuals who embrace lifelong learning are more receptive to new information, more likely to recognize patterns, and better equipped to synthesize diverse ideas. This constant influx of knowledge provides a rich reservoir of information that can be drawn upon when generating new ideas. This learning doesn’t have to be formal; it can encompass reading, conversations, travel, or any experience that exposes one to new perspectives and challenges existing assumptions.
Examples of Curious Innovators
Numerous individuals throughout history have demonstrated the power of curiosity in driving innovation. Marie Curie, driven by an insatiable curiosity about radioactivity, revolutionized our understanding of the atom and earned two Nobel Prizes. Similarly, Thomas Edison’s relentless experimentation and questioning of existing technologies led to countless inventions, transforming daily life. These individuals exemplify how a deep-seated curiosity can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements.
Fostering Curiosity: Different Approaches
Cultivating curiosity in individuals can be approached in various ways. Formal education plays a vital role in encouraging critical thinking and questioning. Experiential learning, such as travel and hands-on projects, provides opportunities for firsthand exploration and discovery. Encouraging a culture of open dialogue and constructive criticism within teams can foster a climate where questioning is valued and new ideas are welcomed.
Overcoming Biases and Preconceived Notions
Biases and preconceived notions can significantly hinder creative thinking by limiting the range of possibilities considered. Individuals often fall into the trap of relying on established patterns and rejecting unconventional ideas. To overcome these barriers, conscious effort is needed to actively challenge existing assumptions and explore alternative perspectives. Seeking out diverse viewpoints and actively engaging with counterarguments can help break free from ingrained biases.
Closed-Minded vs. Open-Minded Approaches
| Closed-Minded Approach | Open-Minded Approach |
|---|---|
| Reliance on established procedures and routines. | Active seeking of diverse viewpoints and perspectives. |
| Limited consideration of alternative solutions. | Embracing ambiguity and uncertainty. |
| Example: A team solely focused on existing marketing strategies, ignoring new social media trends. | Example: A team actively researching new social media trends and experimenting with different approaches. |
| Example: A researcher dismissing data that contradicts their initial hypothesis. | Example: A researcher actively seeking out data that might challenge their initial hypothesis. |
| Example: A student refusing to consider a different approach to a problem after encountering one solution. | Example: A student exploring various approaches to a problem and seeking feedback from peers. |
Proactive Information Gathering: 10 Habits People Who Can Always Generate Great Ideas

Cultivating a mindset of proactive information gathering is crucial for generating innovative ideas. Simply passively absorbing information isn’t enough; actively seeking out diverse sources and then strategically processing that information allows for a richer, more nuanced understanding of the world around us. This leads to a more comprehensive knowledge base, enabling the identification of connections and patterns that might otherwise remain hidden.A key aspect of idea generation lies in understanding how to move beyond readily available information to uncover novel perspectives and insights.
This process often involves exploring unconventional sources and methods, and critically evaluating the information encountered to filter out irrelevant data and focus on what’s truly valuable. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of complex issues and encourages the development of unique perspectives, ultimately leading to a higher likelihood of generating creative solutions.
Strategies for Finding and Processing Information
Effective information gathering involves a combination of targeted searching and critical evaluation. Begin by defining the specific area of interest. Then, systematically explore a range of information sources, ensuring diversity to avoid biases. Developing a structured approach to processing information is essential. This involves taking detailed notes, identifying key concepts, and outlining connections between different pieces of information.
Thinking outside the box and generating brilliant ideas isn’t just for adults; fostering creativity in kids is key! One crucial element to nurturing this ability is a strong foundation in reading. Learning how to teach kids to read effectively, as outlined in this helpful guide how to teach kids to read , is fundamental to developing critical thinking skills.
After all, reading exposes children to diverse perspectives and new ideas, which in turn, sparks creativity and fuels innovative thought processes. These are just a few of the many steps to cultivating the 10 habits of idea generators in children and adults alike.
A well-organized system for storing and retrieving this information is also vital for future reference and analysis.
Categorization of Information Sources
To maximize the potential for generating new ideas, it’s important to categorize information sources based on their potential to spark new connections and perspectives. This categorization allows for a more focused and effective search, enabling the identification of sources most likely to provide novel insights.
- Academic Journals and Research Papers: These sources provide in-depth analysis and findings from rigorous studies. They offer valuable insights into current research and established theories, providing a foundation for developing new ideas based on existing knowledge. Examples include publications from reputable scientific societies and university presses.
- Industry Reports and Market Analysis: These sources often present data and trends relevant to specific sectors. They can offer insights into emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, and market dynamics, which can be helpful in identifying potential opportunities and challenges.
- News Articles and Media Outlets: News reports, blogs, and social media posts provide real-time information on current events, trends, and public discourse. These can provide context and spark ideas about emerging issues, societal concerns, and innovative approaches.
- Personal Networks and Conversations: Networking with individuals from diverse backgrounds can open up new perspectives and sources of information. Conversations, both formal and informal, can provide valuable insights into diverse viewpoints, potential challenges, and opportunities.
Synthesizing Information from Diverse Sources
The power of proactive information gathering lies in its ability to connect seemingly disparate pieces of information. Synthesizing information from various sources allows for the identification of unexpected connections and the development of innovative ideas. This process involves comparing and contrasting different perspectives, identifying patterns and inconsistencies, and constructing new frameworks based on the integrated information.
| Source Type | Potential Idea Triggers | Example Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Journals | Theoretical frameworks, research gaps, methodological improvements | Nature, Science, specific journals in the field of interest |
| Industry Reports | Market trends, competitive analysis, emerging technologies | Reports from market research firms, industry associations |
| News Articles | Current events, societal trends, public discourse | The New York Times, The Economist, relevant blogs |
| Personal Networks | Unique perspectives, practical applications, potential partnerships | Mentors, colleagues, industry contacts |
Connecting the Dots
The ability to connect seemingly disparate ideas is a cornerstone of innovation. It’s not enough to simply gather information; you need to forge connections between seemingly unrelated concepts to unlock truly groundbreaking solutions. This process, often described as “lateral thinking,” involves a unique way of looking at the world, spotting patterns, and recognizing the hidden relationships between diverse fields of knowledge.
This is a crucial skill for anyone seeking to generate truly innovative ideas.Connecting seemingly unrelated concepts can lead to novel insights and solutions by fostering unexpected breakthroughs. When you bridge gaps between different disciplines, you create fertile ground for creativity and innovation. This often results in the creation of entirely new approaches to existing problems or the development of entirely new products or services.
Ever wondered how some folks just seem to churn out brilliant ideas? It might be more than just luck; it’s likely a combination of focused habits. One key element, I’ve noticed, is mindful engagement with the world around them. Think about the 5 benefits of mindful eating – paying close attention to your body’s signals, savoring each bite, and being present in the moment.
This same approach, applied to problem-solving, can unlock creativity. Ultimately, those who consistently generate great ideas likely embrace a blend of mindful habits, constantly seeking new perspectives and connections. Developing these 10 habits is key to boosting your own creative potential. 5 benefits mindful eating
This ability to see the “big picture” is often the key differentiator between a good idea and a truly great one.
Recognizing Patterns and Connections
To effectively connect the dots, you need a keen eye for patterns and relationships. This involves actively seeking out connections between different pieces of information, regardless of their apparent relevance. Consider how different fields of study can intersect. For instance, the principles of aerodynamics, which are fundamental to aeronautical engineering, can also be applied to the design of more efficient sports equipment.
This cross-disciplinary approach is often the spark for revolutionary ideas. A meticulous approach to information gathering and analysis is essential for recognizing these patterns.
Methods for Brainstorming and Idea Generation
Various techniques can be used to encourage the connection of seemingly unrelated ideas. One powerful method is to use a mind map. This visual tool allows you to explore connections between concepts in a non-linear fashion. Starting with a central idea, you can branch out to related concepts, then to sub-concepts, creating a web of interconnected ideas.
Mind Mapping for Idea Organization
A mind map is a visual tool for organizing ideas and connections. It’s a non-linear approach to brainstorming, allowing you to visually represent the relationships between concepts. The central idea is placed at the center of the page. Branches radiate outwards from this central concept, each representing a related idea. Sub-branches can then connect to further detail those concepts.
Colors, images, and s can enhance the visual representation and aid in remembering the connections.
Ever wondered about the secret sauce behind those innovative minds? Exploring 10 habits of idea generators reveals some fascinating insights. For example, a healthy lifestyle, like incorporating chia seeds into your diet—check out 8 amazing health benefits of chia seeds you shouldn’t miss —might actually boost creative thinking. Ultimately, these habits, whether about nutrition or other lifestyle factors, can unlock your inner innovator.
Examples of Connecting Disparate Fields
The intersection of seemingly disparate fields has led to numerous groundbreaking innovations. For instance, the application of principles from materials science to the design of clothing has resulted in garments that are both durable and lightweight. Likewise, the integration of principles from neuroscience and computer science has led to the development of more sophisticated artificial intelligence systems. These are just a few examples of how seemingly disparate fields can be combined to create novel solutions.
Experimentation and Iteration
The ability to experiment and iterate on ideas is crucial for innovation. It’s not enough to have a great initial concept; the process of testing, refining, and adapting is what truly distinguishes successful innovators from those who fall short. This iterative approach allows for the incorporation of feedback, the discovery of unforeseen challenges, and the opportunity to dramatically improve the final product or solution.This process isn’t simply about trial and error; it’s a structured, methodical approach to idea development.
It involves understanding how different variables impact the outcome, and continuously adjusting those variables based on observed results. This structured approach ensures that resources and time are not wasted on unproductive paths, and allows for the most effective and efficient refinement of ideas.
The Role of Experimentation in Idea Generation and Refinement
Experimentation serves as a bridge between theoretical concepts and practical application. It allows for a tangible assessment of the viability and potential of an idea, pushing it beyond the realm of abstract thought. Through experimentation, flaws in logic or implementation become apparent, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the project’s complexities. This early identification of potential problems allows for proactive adjustments and the refinement of strategies.
Iterative Processes and Idea Improvement
Iterative processes are fundamental to the improvement of ideas. They involve cycles of testing, analysis, and adjustment, leading to a continuous refinement of the initial concept. Each iteration builds upon the previous one, incorporating insights gleaned from the previous stage. This approach fosters a dynamic feedback loop, transforming ideas from potential into tangible solutions.
Methods for Evaluating and Testing Approaches
A variety of methods can be employed for evaluating and testing different approaches. Quantitative methods, like A/B testing, can provide objective data on the effectiveness of different variations. Qualitative methods, like user interviews and focus groups, offer valuable insights into user perception and experience. A combination of these methods provides a comprehensive picture of the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.
Thorough documentation of each step, including observations and data points, is critical for understanding the evolution of the idea and for identifying patterns.
Comparison of Innovator Approaches to Iterative Improvement
Different innovators employ various approaches to iterative improvement. For example, Henry Ford’s approach to manufacturing involved a series of iterative improvements to the assembly line process. Similarly, Steve Jobs at Apple was known for his relentless focus on user experience and a willingness to iterate on designs based on user feedback. Each innovator’s approach was unique, but the common thread was a commitment to continuous improvement through experimentation and adaptation.
Stages of Experimentation and Corresponding Outcomes
| Stage | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Concept | Formulating the core idea and initial design. | Basic understanding of the problem and a preliminary solution. |
| Pilot Testing | Implementing a small-scale version of the idea. | Identification of initial strengths and weaknesses, potential issues, and areas for improvement. |
| Refinement | Making adjustments based on pilot test results. | Improved design, addressing identified flaws and incorporating user feedback. |
| Large-Scale Testing | Deploying the refined idea on a larger scale. | Validation of the idea’s efficacy in a broader context, and gathering further feedback. |
| Continuous Improvement | Ongoing refinement and adjustment based on feedback and performance data. | Optimized solution, addressing unforeseen challenges and further enhancing user experience. |
Persistence and Resilience
The creative process is rarely a smooth, linear journey. Obstacles, setbacks, and periods of stagnation are inevitable. The ability to persevere through these challenges, maintaining motivation and a willingness to learn from failures, is critical for consistently generating great ideas. True innovation often emerges from the crucible of persistent effort.The key to generating great ideas isn’t just having the initial spark, but nurturing that spark through the inevitable struggles.
This involves understanding that the creative process is a marathon, not a sprint, and recognizing that setbacks are often stepping stones to breakthroughs. Learning to bounce back from these setbacks, and to view failures as valuable learning experiences, is essential for long-term creative success.
The Importance of Perseverance
Sustained effort and a willingness to overcome hurdles are crucial in the creative process. Ideas often require significant refinement, testing, and adaptation. A persistent approach allows creators to navigate these challenges and refine their initial concepts into something truly impactful.
Overcoming Obstacles and Setbacks
Creative blocks and roadblocks are common. Strategies for overcoming these obstacles include seeking diverse perspectives, re-evaluating the problem from different angles, and actively seeking out mentors or collaborators. When facing a seemingly insurmountable obstacle, breaking the problem into smaller, more manageable tasks can be extremely helpful. Also, fostering a growth mindset, embracing challenges as opportunities for learning, and adopting a positive attitude can contribute significantly to navigating setbacks.
Examples of Persistent Innovators
Numerous individuals have demonstrated remarkable persistence despite facing significant challenges. Consider the story of Marie Curie, who relentlessly pursued her research despite societal barriers and personal hardships. Her unwavering dedication to her scientific pursuits resulted in groundbreaking discoveries in radioactivity. Similarly, Steve Jobs, despite facing setbacks and controversies in his career, demonstrated an unparalleled commitment to his vision and the innovative products he created.
These examples underscore the power of unwavering dedication in the face of adversity.
Strategies for Maintaining Motivation
Maintaining motivation during periods of stagnation is a crucial aspect of the creative process. Strategies include setting realistic goals, breaking down larger projects into smaller, achievable steps, and regularly rewarding progress. Engaging in activities that provide inspiration and joy can also help maintain motivation and enthusiasm. Furthermore, surrounding yourself with a supportive network of peers and mentors can provide encouragement and feedback during challenging times.
Learning from Failures
Failures are not setbacks; they are opportunities for growth and refinement. Analyzing failures and identifying the underlying causes is crucial. By understanding why an approach didn’t work, creators can refine their strategies and approaches, potentially leading to a better result in the future. Viewing failures as part of the learning process is key to continuous improvement and innovation.
Taking time to reflect on past failures and extract valuable lessons can lead to significant breakthroughs. Thorough documentation of both successes and failures can serve as a valuable resource for future projects.
Effective Communication and Collaboration
Ideas, like sparks, need the right environment to ignite and flourish. Effective communication and collaboration are the oxygen and fuel that keep the creative fire burning. Without clear channels for sharing thoughts and a supportive environment for joint effort, even the most brilliant ideas can fizzle out. This vital link between individuals is critical for generating groundbreaking solutions and fostering innovation.Effective communication isn’t just about conveying information; it’s about understanding, empathy, and actively listening to different perspectives.
This reciprocal exchange of ideas creates a fertile ground for new insights and allows individuals to build upon each other’s thoughts. Furthermore, the ability to receive and incorporate constructive feedback is essential for refining and improving ideas. Collaboration, in turn, extends this process, allowing diverse viewpoints to combine, and leading to more innovative and robust outcomes.
Importance of Effective Communication in Idea Generation
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful idea generation. It allows for the seamless exchange of information, ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Clear and concise communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that ideas are understood accurately, fostering collaboration and innovation. This clarity enables individuals to build upon existing ideas, refine concepts, and explore potential avenues for development.
Furthermore, effective communication is crucial in conveying the rationale behind an idea, motivating others to understand its potential and contribute their expertise.
Strategies for Sharing Ideas and Receiving Feedback
Sharing ideas effectively requires a structured approach. This involves clearly articulating the core concept, outlining the rationale behind it, and presenting potential solutions or applications. Active listening is just as important as articulating your ideas; actively listening to feedback allows for greater understanding and improvement. Constructive feedback provides valuable insights, helping refine ideas into more practical and effective solutions.
Strategies for receiving feedback should include actively seeking input from others, clarifying any ambiguities, and responding thoughtfully to the feedback received. This iterative process is crucial for the evolution of ideas.
Role of Collaboration in Sparking New Ideas
Collaboration fosters a dynamic environment where diverse perspectives and experiences combine. The interaction between individuals with different backgrounds and expertise leads to a richer understanding of the problem, and the emergence of innovative solutions. This synergy can lead to breakthroughs that would not have been possible through individual efforts. Combining different skill sets, perspectives, and experiences leads to more comprehensive and holistic solutions.
Examples of Successful Collaborations Leading to Groundbreaking Ideas
Numerous collaborations have resulted in revolutionary ideas across various fields. The development of the World Wide Web, for instance, stemmed from the collaboration between various researchers and engineers. Similarly, the creation of groundbreaking medical treatments often involves collaborative efforts between scientists, clinicians, and patients. Such collaborations demonstrate the immense power of diverse minds working together towards a common goal.
Another notable example is the development of the first personal computer, a result of numerous engineers and scientists collaborating to combine different technologies and ideas.
Communication Styles and Their Impact on Idea Generation, 10 habits people who can always generate great ideas
| Communication Style | Description | Impact on Idea Generation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | Clear, concise, and to the point. | Can be efficient, but may miss subtle nuances and perspectives. | Giving a clear presentation of a technical solution. |
| Indirect | Subtle, nuanced, and suggestive. | Can spark creativity, but may lead to misinterpretations if not clearly articulated. | Using metaphors to describe an abstract concept. |
| Collaborative | Encouraging participation and open dialogue. | Fosters diverse perspectives, but may be slower than direct communication. | Brainstorming sessions in a team environment. |
| Authoritarian | Top-down approach with limited feedback. | May stifle creativity and limit the potential for new ideas. | A manager dictating the direction of a project without input. |
Problem-Solving Approach
A problem-solving mindset is crucial for generating great ideas. It’s not just about identifying problems; it’s about approaching them systematically, exploring diverse perspectives, and relentlessly seeking innovative solutions. This proactive engagement with challenges often leads to breakthroughs that wouldn’t be possible through passive observation. A strong problem-solving foundation allows individuals to move beyond superficial solutions and delve into the root causes, ultimately fostering a more creative and impactful approach to idea generation.This approach encourages critical thinking, analysis, and the ability to break down complex issues into manageable components.
It cultivates a willingness to experiment, iterate, and learn from failures, all essential elements in the creative process. Furthermore, a well-developed problem-solving skillset enhances collaboration and communication, as individuals can articulate their thought processes and effectively engage with others in finding solutions.
Problem-Solving Mindset and Creative Thinking
A problem-solving mindset fosters creative thinking by encouraging a structured and analytical approach to challenges. This structured approach allows individuals to systematically dissect problems, identify underlying causes, and explore diverse perspectives. This process often leads to novel solutions that wouldn’t emerge from a purely intuitive or spontaneous approach. Individuals with a strong problem-solving aptitude are often more adept at identifying the root causes of a problem rather than just the symptoms, which can lead to more effective and innovative solutions.
Examples of Individuals Using Problem-Solving
Numerous individuals have leveraged a problem-solving approach to develop groundbreaking solutions. For example, Marie Curie’s relentless pursuit of isolating radium, despite facing significant challenges in laboratory conditions, exemplifies a profound commitment to problem-solving. Similarly, Henry Ford’s innovative approach to mass production, tackling issues like efficient assembly lines and standardized parts, led to revolutionary advancements in manufacturing. These examples highlight how a focused problem-solving approach can lead to remarkable outcomes.
Problem-Solving Frameworks for Idea Generation
Various problem-solving frameworks can facilitate idea generation. The scientific method, with its emphasis on observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and analysis, is a powerful tool for generating creative solutions. The design thinking process, which involves empathizing with users, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing, is another effective framework. These frameworks provide a structured pathway to tackle challenges, encouraging creative thinking and ultimately, the generation of innovative ideas.
Defining Problems Clearly and Comprehendssively
Clearly defining a problem is paramount for effective problem-solving. This involves understanding the context, identifying the root causes, and articulating the desired outcome. A poorly defined problem often leads to misdirected efforts and ineffective solutions. Consider a business facing declining sales. A superficial understanding might only focus on lowering prices.
However, a comprehensive definition might uncover underlying issues like changing consumer preferences, ineffective marketing strategies, or a declining brand image.
Problem-Solving Techniques
- Root Cause Analysis: This technique involves systematically identifying the underlying causes of a problem, moving beyond superficial symptoms. By digging deeper, you can develop more effective and sustainable solutions.
- Brainstorming: This technique encourages the generation of a large number of ideas without judgment, fostering a creative environment for problem-solving.
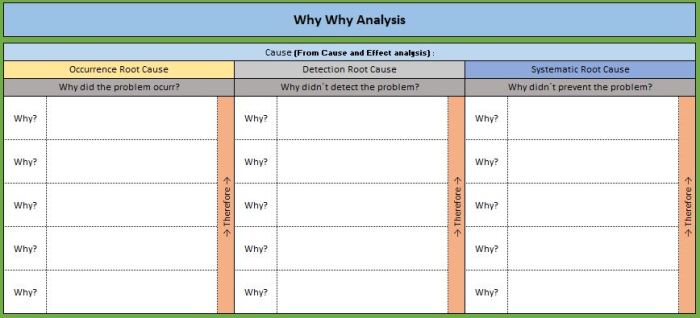
- The 5 Whys: This technique repeatedly asks “why” to uncover the root causes of a problem. Each answer leads to a deeper understanding of the underlying issue.
- Lateral Thinking: This technique encourages unconventional approaches to problem-solving, fostering innovative and out-of-the-box solutions.
- Mind Mapping: This technique visualizes ideas and connections, enabling a more holistic understanding of the problem and its potential solutions.
Problem-Solving Techniques – Hierarchical Table
| Technique | Description | Connection to Other Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Root Cause Analysis | Identifying underlying causes of a problem | Often precedes and informs other techniques like 5 Whys. |
| Brainstorming | Generating many ideas without judgment | Can be used in conjunction with other techniques to generate diverse perspectives. |
| The 5 Whys | Repeatedly asking “why” to uncover root causes | Effective in combination with Root Cause Analysis, to delve deeper into problem origin. |
| Lateral Thinking | Unconventional approaches to problem-solving | Often used after brainstorming, to find innovative solutions. |
| Mind Mapping | Visualizing ideas and connections | Can be a helpful tool for organizing ideas generated through brainstorming and other techniques. |
Embracing Imperfection

Embracing imperfection is a crucial aspect of cultivating a creative mindset. Great ideas often emerge from initial concepts that are far from perfect. A willingness to accept and even celebrate flaws in the early stages can unlock a cascade of innovative solutions. This approach allows for a more flexible and adaptable creative process, where adjustments and improvements can be made along the way.
It’s about acknowledging that the journey of creation is rarely a straight line, but rather a winding path of exploration and refinement.A strong foundation for creativity is built on the ability to view initial ideas as stepping stones, not as definitive endpoints. This perspective fosters a growth mindset, encouraging experimentation and the iterative process of improvement. The journey of developing a revolutionary idea is rarely a direct path from concept to completion.
Instead, it typically involves numerous iterations, revisions, and unexpected detours.
Initial Flawed Ideas Leading to Valuable Contributions
Many groundbreaking innovations started as imperfect prototypes or concepts. The initial versions often faced criticism or skepticism, yet perseverance and refinement transformed them into valuable contributions. The first iterations of the personal computer, for instance, were bulky, slow, and lacked many of the features we now consider essential. However, through relentless experimentation and iteration, these early models evolved into the powerful and ubiquitous devices we use today.
Similarly, the first iterations of the internet were far less user-friendly and accessible than their current versions.
Strategies for Overcoming the Fear of Mistakes
Fear of making mistakes can stifle creativity. One strategy to overcome this fear is to create a safe space for experimentation. This can be achieved by surrounding oneself with supportive individuals who encourage risk-taking and celebrate effort over immediate results. Another approach is to reframe mistakes as learning opportunities. When a concept doesn’t pan out as expected, instead of dwelling on the failure, analyze what went wrong and identify areas for improvement.
A crucial part of this is acknowledging that mistakes are inevitable and a natural part of the creative process.
The Importance of Risk-Taking in Generating Novel Ideas
Risk-taking is inherently linked to the generation of novel ideas. Individuals who are willing to step outside their comfort zones and explore unconventional approaches are more likely to discover innovative solutions. This willingness to embrace the unknown often leads to breakthroughs that might otherwise remain hidden. It’s about recognizing that the potential for reward often accompanies the possibility of failure.
Detailed Example of a Successful Idea Initially Criticized
The development of the first commercially successful digital music player, the iPod, is a prime example. Initial concepts faced criticism for their limited storage capacity and lack of compatibility with various devices. However, Apple’s engineers persisted, focusing on refining the user interface and improving storage capacity. They iterated on the design, eventually creating a user-friendly device that became a cultural phenomenon.
Their ability to embrace imperfections, learn from setbacks, and adapt to evolving market needs ultimately led to a product that revolutionized the music industry. By focusing on user experience and addressing the limitations of the initial concept, the iPod evolved from a flawed idea into a revolutionary product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, generating great ideas is not a solitary endeavor but a multifaceted process. By cultivating curiosity, actively seeking information, connecting ideas, experimenting, persisting, and collaborating, individuals can unlock their creative potential. Embracing imperfection and a problem-solving mindset are crucial ingredients for a constant flow of novel ideas. Ultimately, fostering these habits can lead to a transformative impact on personal and professional endeavors.